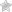Remote connection from pgadmin4 to a Linux server running PostgreSQL:

To establish a remote connection from pgadmin4 to a Linux server running PostgreSQL,
Follow the below steps:
1. Install Pgadmin4: First install pgadmin4 on your local machine. You can download it from the official website (https://www.enterprisedb.com/downloads/postgres-postgresql-downloads) and follow the instructions for the installation.
2. Enable remote access on the Linux server:
To allow remote connections, you need to modify the PostgreSQL server’s configuration file.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
[postgres@postgres1 ~]$ cd /u01/data1 [postgres@postgres1 data1]$ ls base pg_dynshmem pg_logical pg_replslot pg_stat pg_tbls global pg_hba.conf pg_multixact pg_serial pg_stat_tmp pg_twop pg_commit_ts pg_ident.conf pg_notify pg_snapshots pg_subtrans PG_VERS [postgres@postgres1 data1]$ vi postgresql.conf |
Modify the below configurations then save and exit the file.
|
1 2 |
listen_address='*' port=5432 |
Now, restart the cluster to apply changes.
|
1 |
[postgres@postgres1 data1]$ pg_ctl restart |
3. Modify the pg_hba.conf file:
Navigate through the data directory and open the ‘pg_hba.conf’ file.
|
1 |
[postgres@postgres1 data1]$ vi pg_hba.conf |
This file controls the authentication and access rules for PostgreSQL connections.
The entry should specify the IP address or subnet range of the client machine.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
# TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD # "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only local all all trust # IPv4 local connections: host all all 192.168.0.103/0 trust # IPv6 local connections: host all all ::1/128 trust |
Here we alter the IPv4 local connections.
TYPE – host
Database – all #to access all databases
User – all # all users can access the database
ADDRESS – 192.168.0.103/0 # provide your client (windows) IP address
Method – trust # no password needed
Now reload the cluster to modify changes
|
1 |
[postgres@postgres1 data1]$ pg_ctl reload |
4. Configure firewall settings:
To allow connection from outside we should alter the firewall configuration.
Firstly, switch to the root user
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
[postgres@postgres1 ~]$ su – root Now use the following to stop the firewall [root@postgres1 ~]# service iptables stop iptables: Setting chains to policy ACCEPT: nat mangle file[ OK ] iptables: Flushing firewall rules: [ OK ] iptables: Unloading modules: [ OK ] Check the status by using following command [root@postgres1 ~]# service iptables status |
iptables: Firewall is not running.
Setting up password to user:
To alter password to a user. Connect to the plsql database and run the following command.
|
1 |
postgres=# alter user postgres with password 'postgres'; |
ALTER ROLE
5. Connect to the remote Server using pgadmin4:
Follow the below steps to Launch Pgadmin4 on your local machine.
♦ Click on “Add New Server” in the top-left corner and select “Create” > “Server”.
♦ Provide a name for the server.
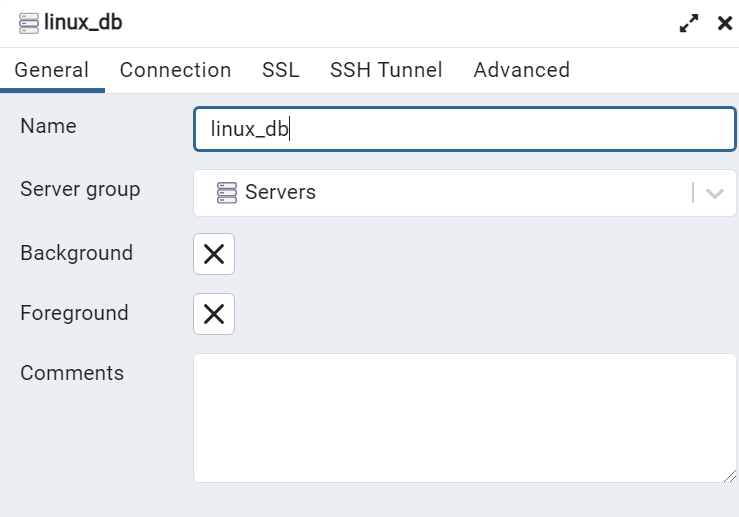
♦ In the “Connection” tab, enter the following information:
Here, Host name/address: IP address of the Linux server.
PORT: PostgreSQL port
Maintenance database: name of the database you want to connect to.
Username: PostgreSQL username with access to the database.
Click on “Save” to save changes.
Now you can see that linux_db server can access the database in Linux server.
Author : Prudhvi Teja |
LinkedIn : http://linkedin.com/in/prudhvi-teja-nagabhyru-715052224
Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the above information. Please click here to subscribe for further updates
KTExperts is always active on social media platforms.
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/ktexperts/
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/company/ktexperts/
Twitter : https://twitter.com/ktexpertsadmin
YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/c/ktexperts
Note: Please test scripts in Non Prod before trying in Production.