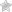DATA TYPES IN CQL
 The Cassandra Query Language, or CQL, is supported by Apache Cassandra. Cassandra Apache The categories of data known as data types specify the kinds of data that can be kept in a variable or object. Programmers instruct the compiler on how to interpret, store, and use data by providing a data type.
The Cassandra Query Language, or CQL, is supported by Apache Cassandra. Cassandra Apache The categories of data known as data types specify the kinds of data that can be kept in a variable or object. Programmers instruct the compiler on how to interpret, store, and use data by providing a data type.
CQL is a typed language and supports a rich set of data types, including native types, collection types, user-defined types, tuple types, and custom types.
Strong typing is used in the Cassandra Query Language (CQL), where variables are given a defined type instead than depending on the compiler to deduce the intended operation from the value. Integrated Cassandra Numerical kinds, collection types, string types, and binary large objects (BLOBs) for byte-array data are examples of data types. Additionally, CQL allows custom data types.
NATIVE TYPES:
Cassandra Data Types are classified into native types, collection types, tuple types, user-defined types, and custom types.
| Type | Constants supported | Description |
| ascii | string | ASCII character string |
| bigint | integer | 64-bit signed long. |
| blob | blob | Arbitrary bytes (no validation) |
| boolean | boolean | Either true or false |
| counter | integer | Counter column (64-bit signed value). See counters for details. |
| date | integer, string | A date (with no corresponding time value). See dates below for details. |
| decimal | integer, float | Variable-precision decimal |
| double | integer float | 64-bit IEEE-754 floating point |
| duration | duration, | A duration with nanosecond precision. See durations below for details. |
| float | integer, float | 32-bit IEEE-754 floating point |
| inet | string | An IP address, either IPv4 (4 bytes long) or IPv6 (16 bytes long). Note that there is no inet constant, IP address should be input as strings. |
| int | integer | 32-bit signed int |
| smallint | integer | 16-bit signed int |
| text | string | UTF8 encoded string |
| time | integer, string | A time (with no corresponding date value) with nanosecond precision. See times below for details. |
| timestamp | integer, string | A timestamp (date and time) with millisecond precision. See timestamps below for details. |
| timeuuid | uuid | Version 1 UUID, generally used as a “conflict-free” timestamp. Also see timeuuid-functions. |
| tinyint | integer | 8-bit signed int |
| uuid | uuid | A UUID (of any version) |
| varchar | string | UTF8 encoded string |
| varint | integer | Arbitrary-precision integer |
COLLECTION DATA TYPES:
CQL supports three kinds of collections: maps, sets and lists. The types of those collections are defined by:
Cassandra Map Data Type – A sorted set of key-value pairs with unique keys, sorted by the key.
Cassandra Set Data Type – A sorted collection of unique values.
Cassandra List Data Type – A collection of non-unique values, ordered by their position in the list. Sets are generally more efficient than Lists if the values can be unique.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
collection_type::= MAP '<' cql_type',' cql_type'>' | SET '<' cql_type '>' | LIST '<' cql_type'>' and their values can be inputd using collection literals: collection_literal::= map_literal | set_literal | list_literal map_literal::= '\{' [ term ':' term (',' term : term)* ] '}' set_literal::= '\{' [ term (',' term)* ] '}' list_literal::= '[' [ term (',' term)* ] ']' |
Note however that neither bind_marker nor NULL are supported inside collection literals.
Author : Neha Kasanagottu |
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/in/neha-kasanagottu-5b6802272
Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the above information. Please click here to subscribe for further updates.
KTExperts is always active on social media platforms.
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/ktexperts/
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/company/ktexperts/
Twitter : https://twitter.com/ktexpertsadmin
YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/c/ktexperts
Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/knowledgesharingplatform
Note: Please test scripts in Non Prod before trying in Production.