Dear Readers,
In this article,we will see Amazon EFS (Elastic File System) in AWS .

Steps to Follow
- Create EFS (Elastic File System).
- Launch 2 Linux Servers.
- Assign default security group to First Linux Server “Linux – 1”.
- Connect to first Linux Server “Linux – 1” terminal through putty.
- Provide default security group to Second Linux Server “Linux – 2”.
- Connect to Second Linux Server “Linux – 2” terminal through putty.
- Create Mount point for first Linux Server “Linux – 1”
- Make Mount Directory.
- Copy mount Command from EFS an Paste Mount command in Linux terminal.
- Make file in Mount Directory.
- Create Mount point for first Linux Server “Linux – 2”.
- Make Mount Directory.
- Copy mount Command from EFS an Paste Mount command in Linux terminal.
- Make file in Mount Directory and Verify files in the mount directory.
Amazon EFS (Elastic File System)
Amazon EFS provides scalable file storage for use with Amazon EC2.
You can create an EFS file system and configure your instances to mount the file system. You can use an EFS file system as a common data source for workloads and applications running on multiple instances.
Note
Amazon EFS is not supported on Windows instances.
- Create EFS (Elastic File System)
First, we need to AWS Console page by using below link.
https://aws.amazon.com/console/
Click on sign in to Console button.
Logging to aws account
Provide username and password then click on sign in.
Enter to AWS Management Console
We can see the AWS Management Console Dashboard.
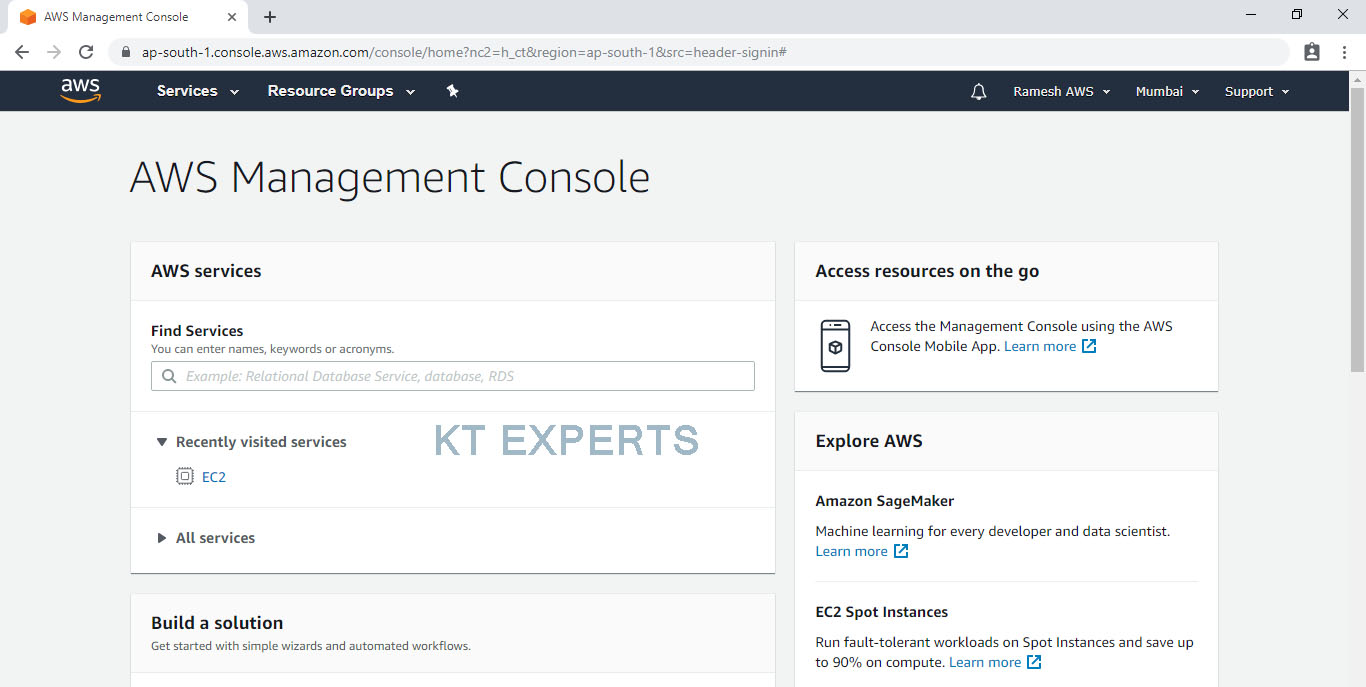
Go to Services, Click on EFS in the Storage Module.
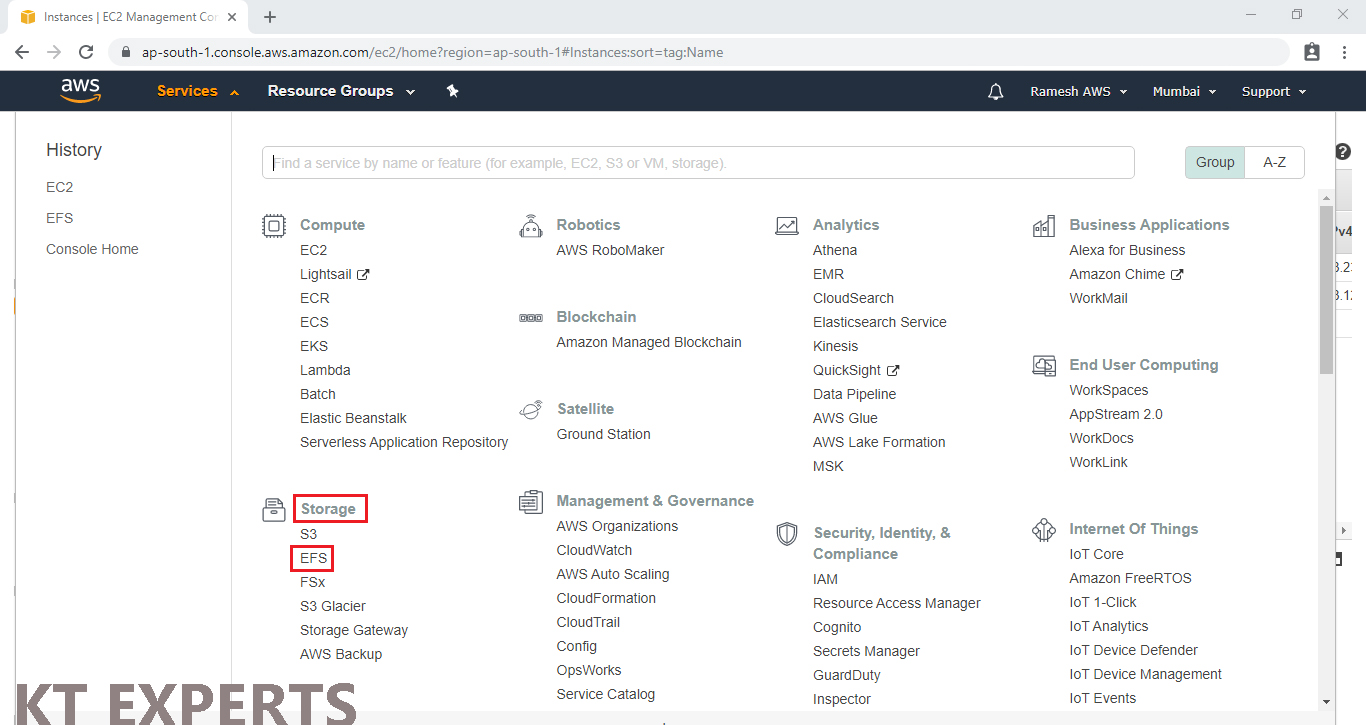
Click on Create file system.

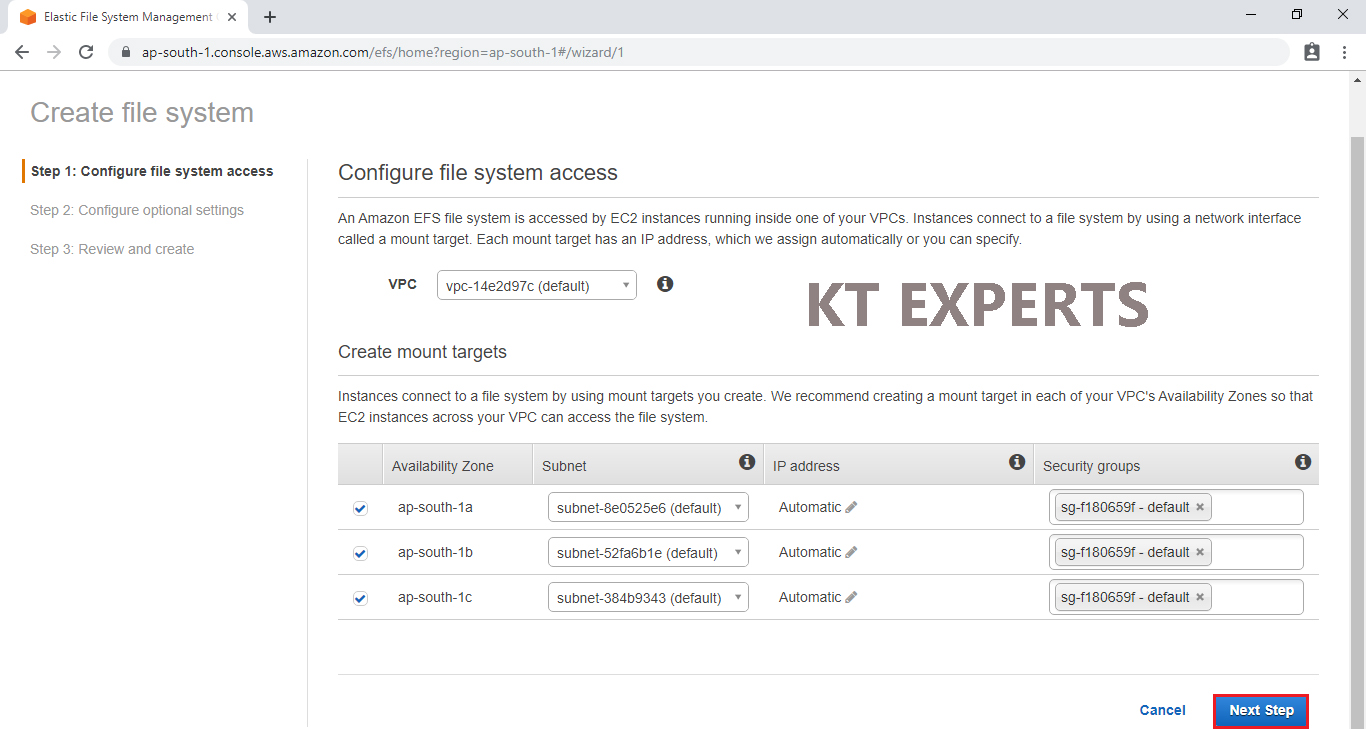
Click on Next Step.
Specify the name for the EFS “My EFS”.
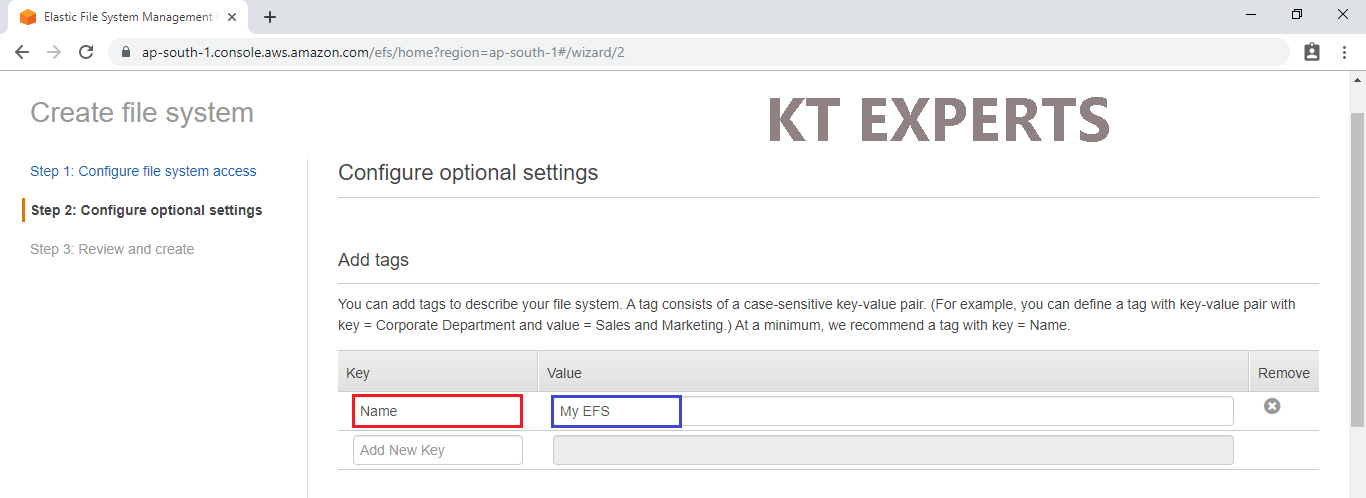
Click on Next Step.
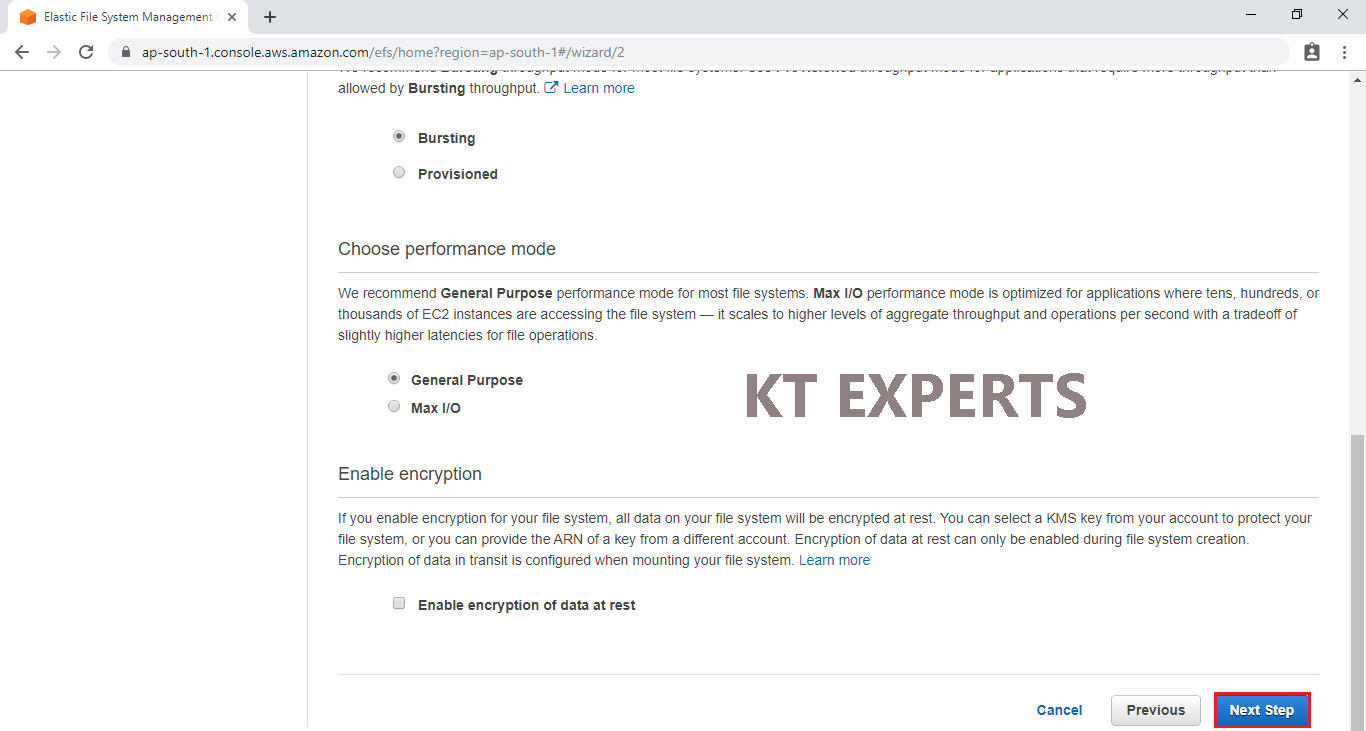
Click on Create file system.
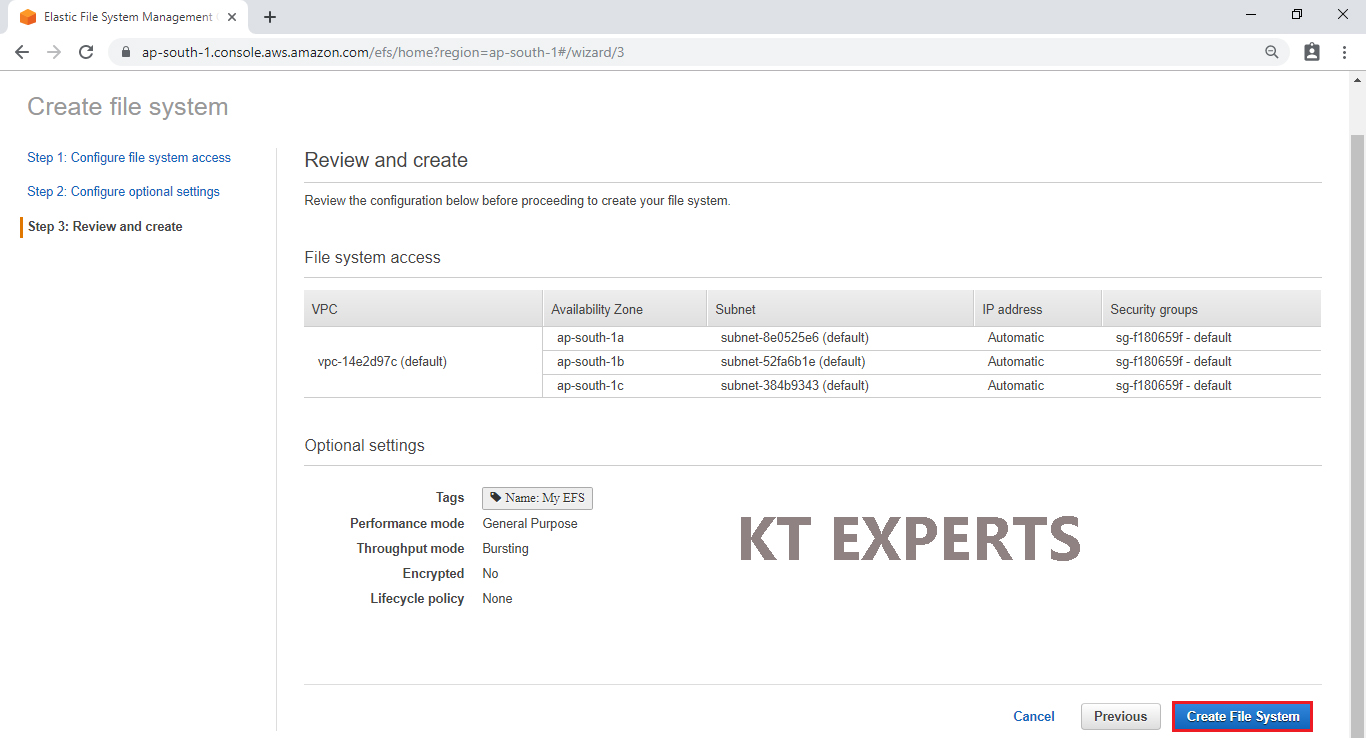
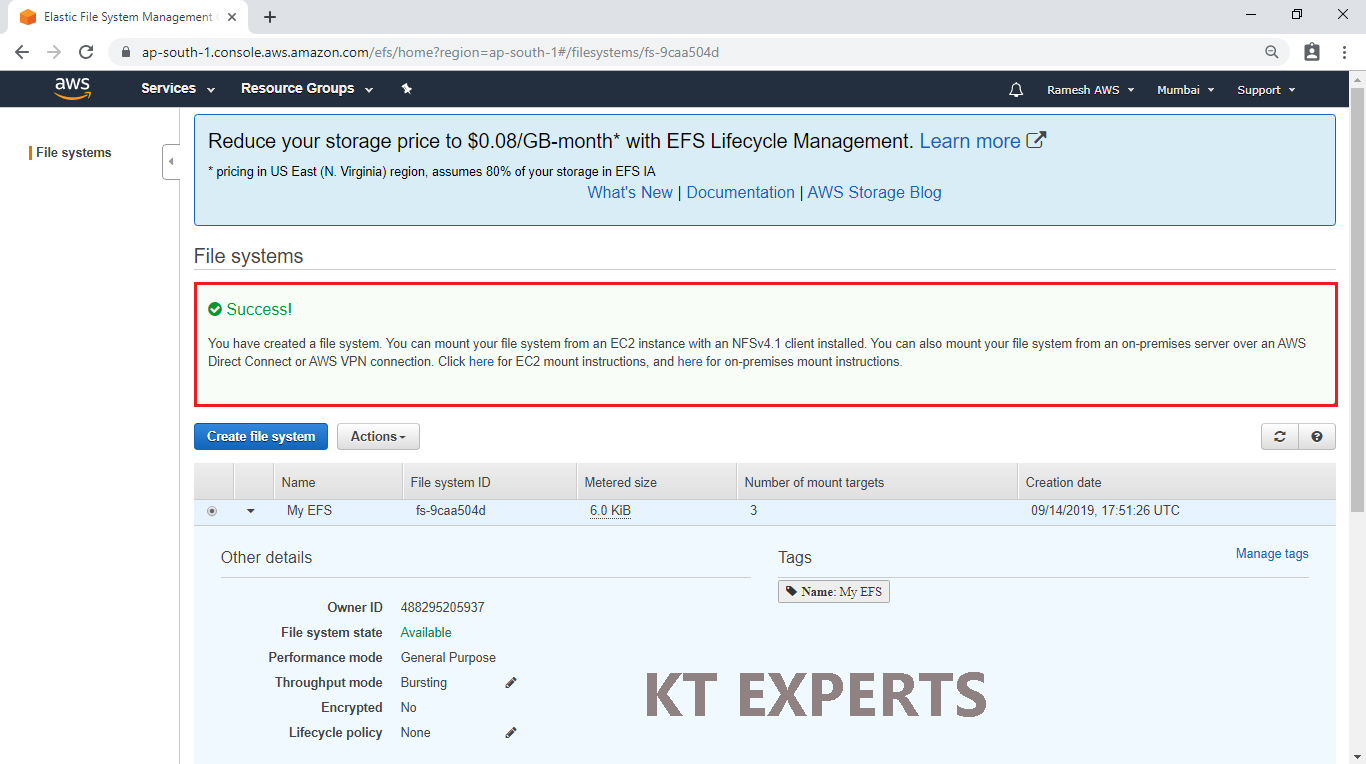
The Elastic file system “My EFS” has been created successfully.
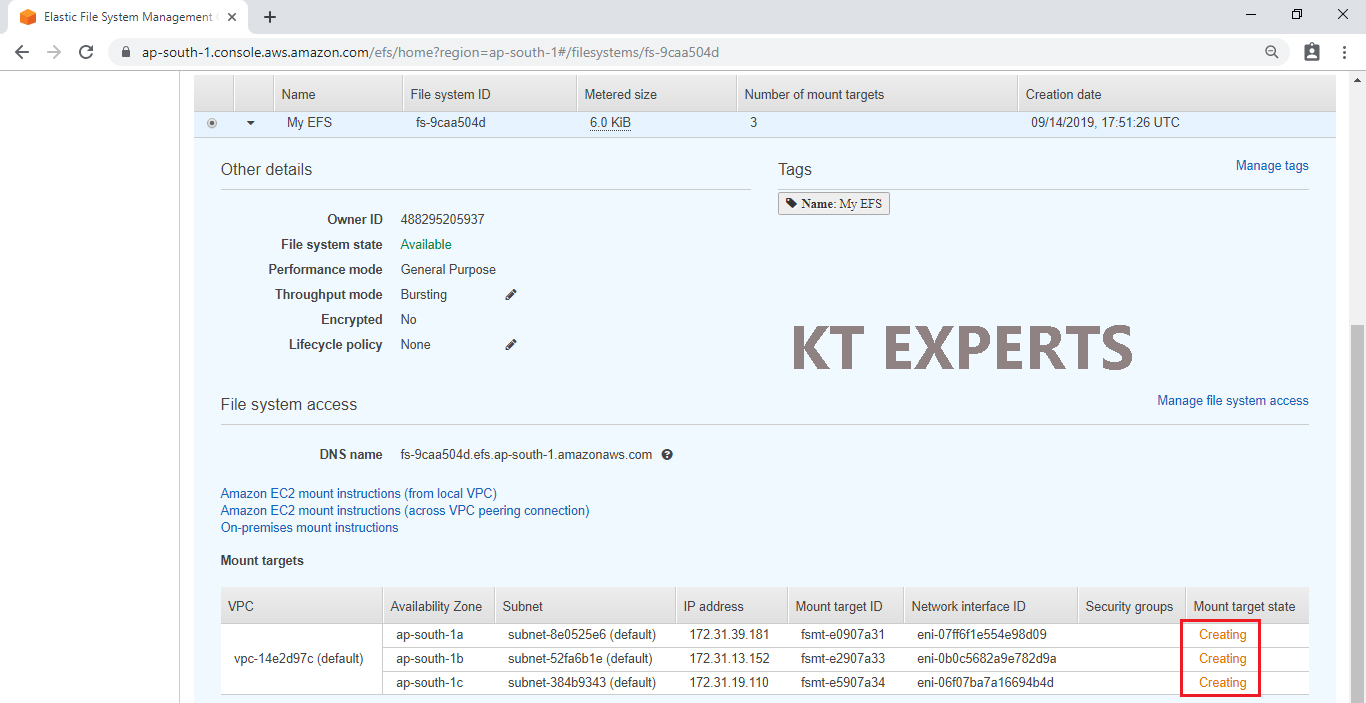
The mount target state is creating now it will take some time to create.
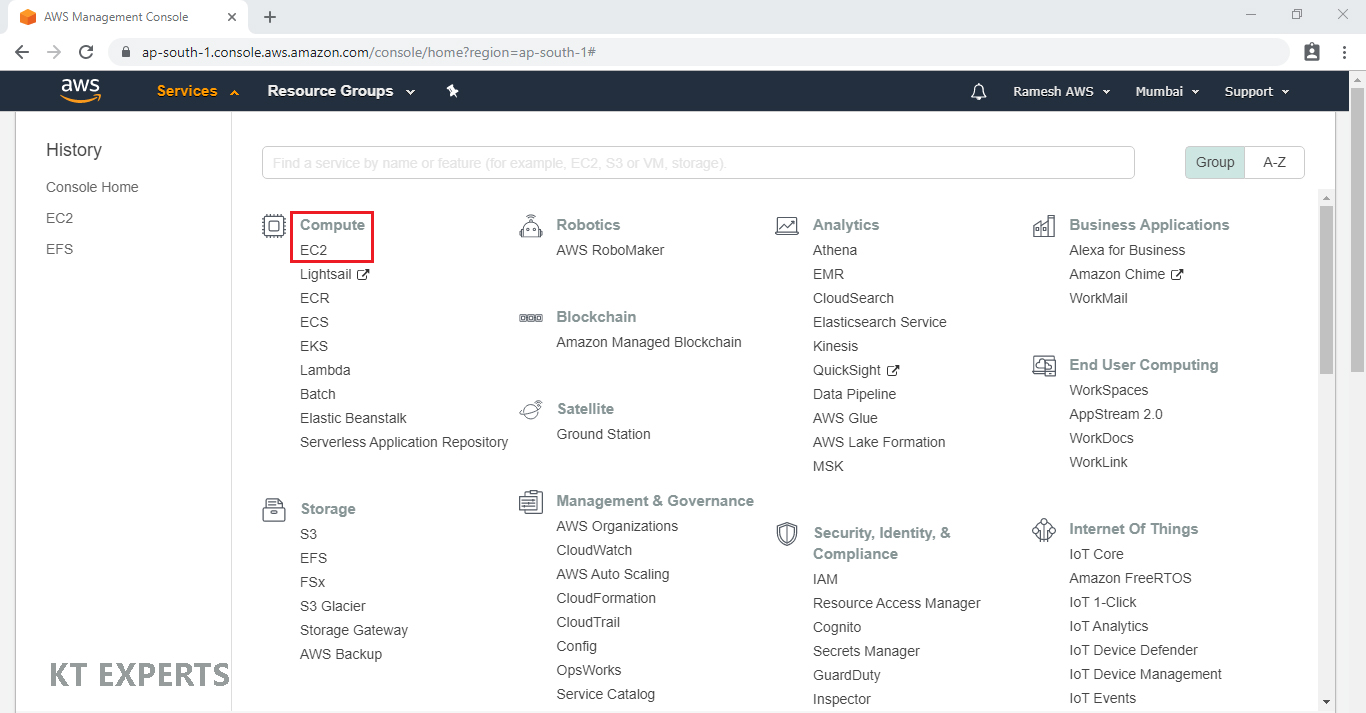
Launch two Linux Servers
Go to Services, under the compute module click EC2 service to open.
Create and Configure a Virtual Machine
We can see EC2 Dashboard by default one security group is available and click on Launch Instance.
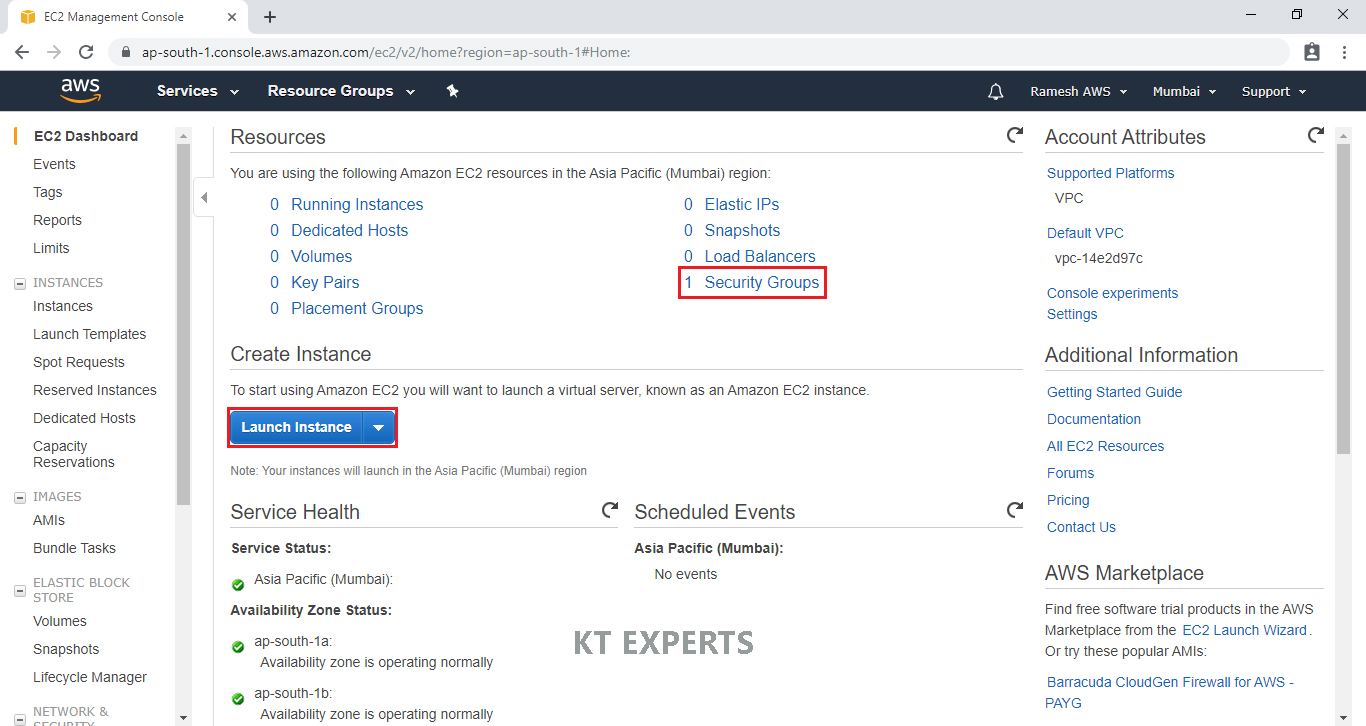
Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
Select the Operating system of the EC2 instance by choosing any of the Amazon Machine Images (AMI). Select the Microsoft Amazon Linux AMI.
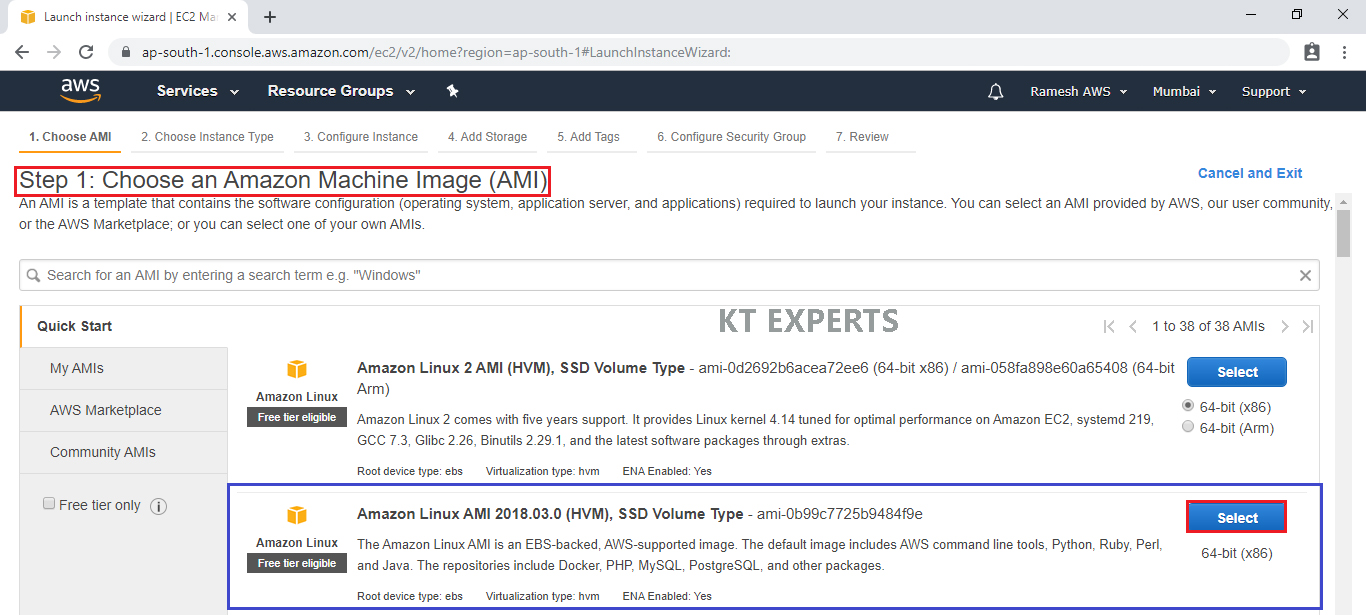
Choose an Instance type
Choose the Type of instance depending on your requirements.
Instance types comprise of varying combinations of CPU, memory, storage, and networking capacity so you can choose the appropriate mix for your applications.
select the default option of t2. micro – this instance type is covered within the free tier. Then click on Configure Instance Details.
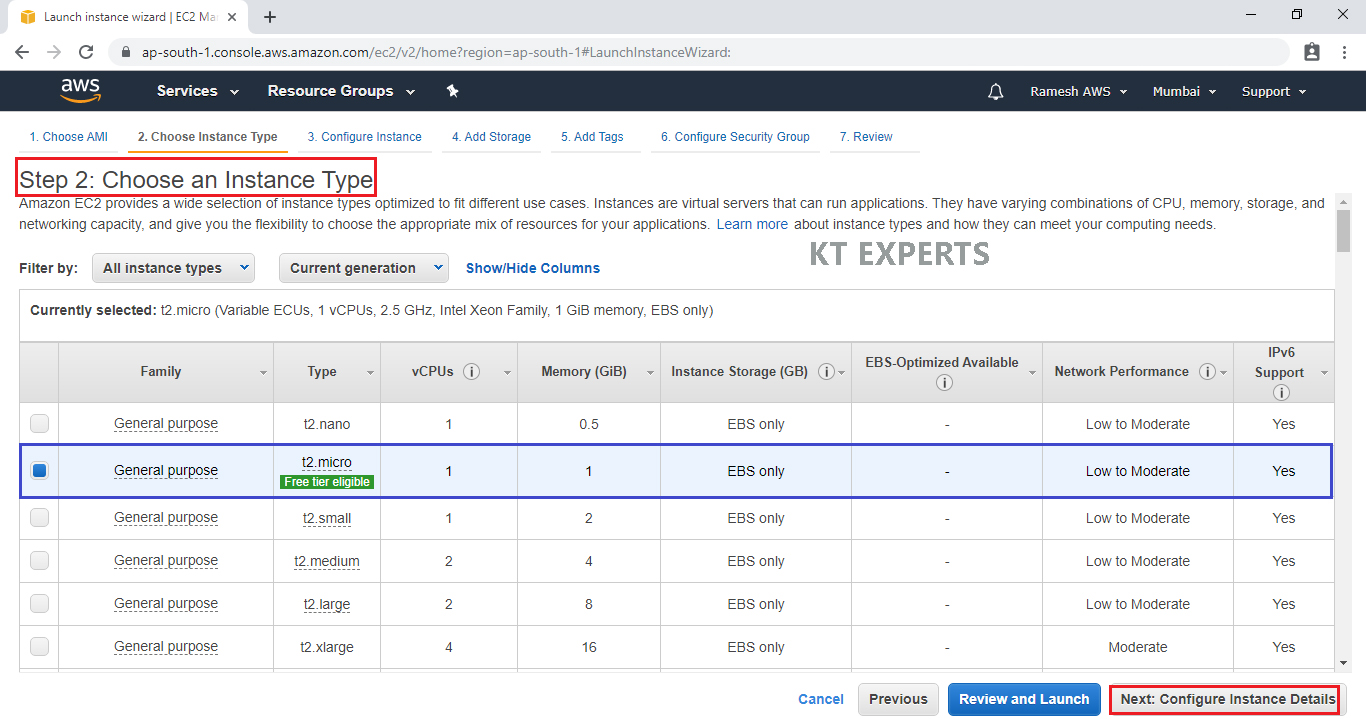
Configure Instance Details
Configure EC2 instance details as per requirements of your environment.
Here we select 2 instances in the number of instances to create 2 instances at once.
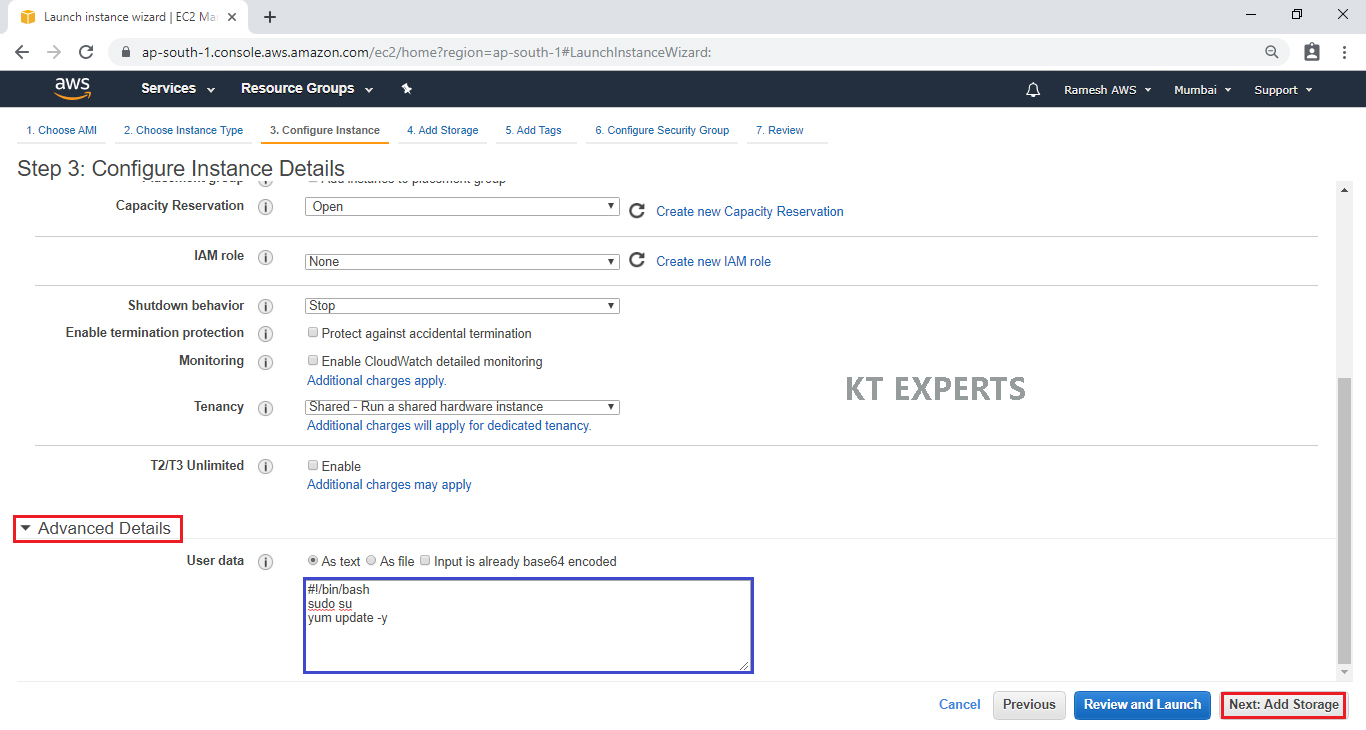
Go Advanced Details and add some commands in user data.
Click on Add storage.
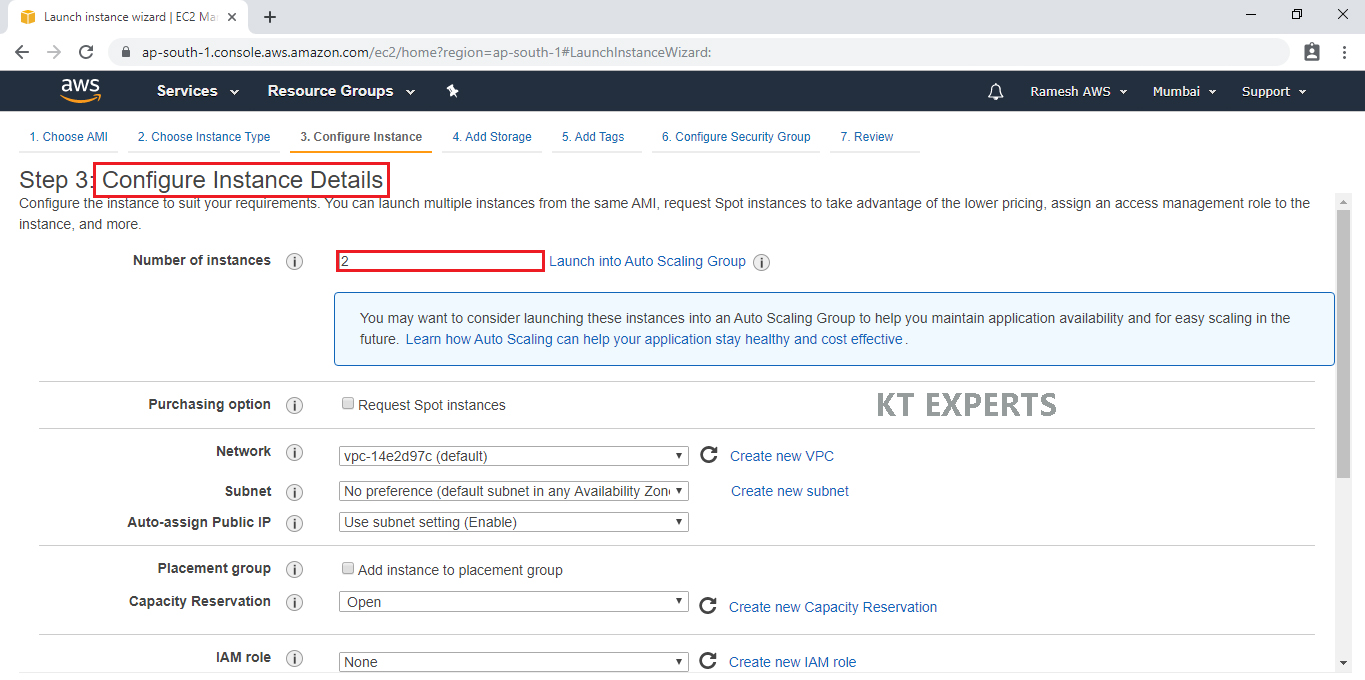
Add Storage
Add a new volume if two drives are required.
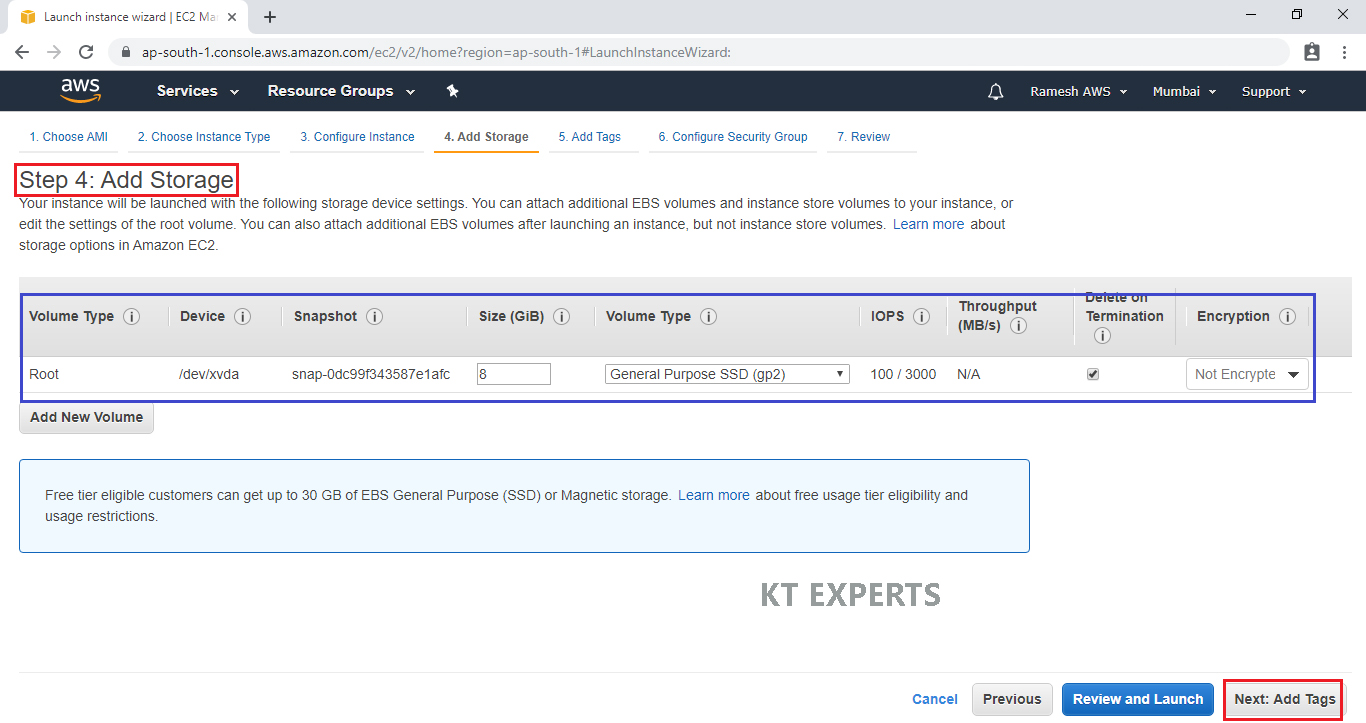
Add Tags
Tags assist in easier identification and classification of the various instances in your AWS environment.
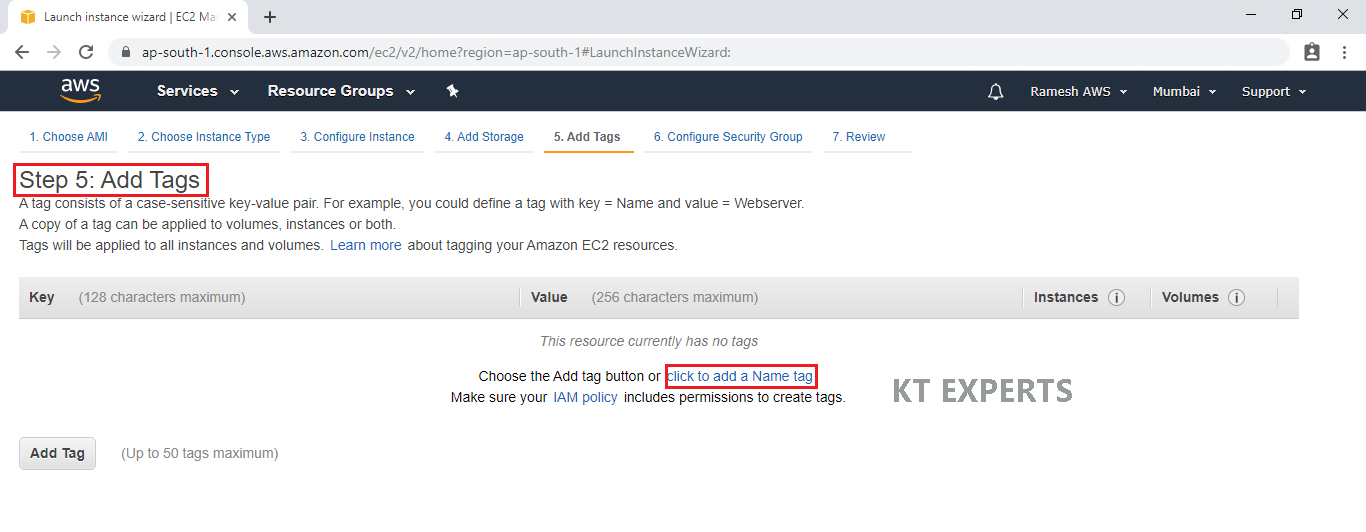
Provide the name for the Linux virtual machine for easier understanding.
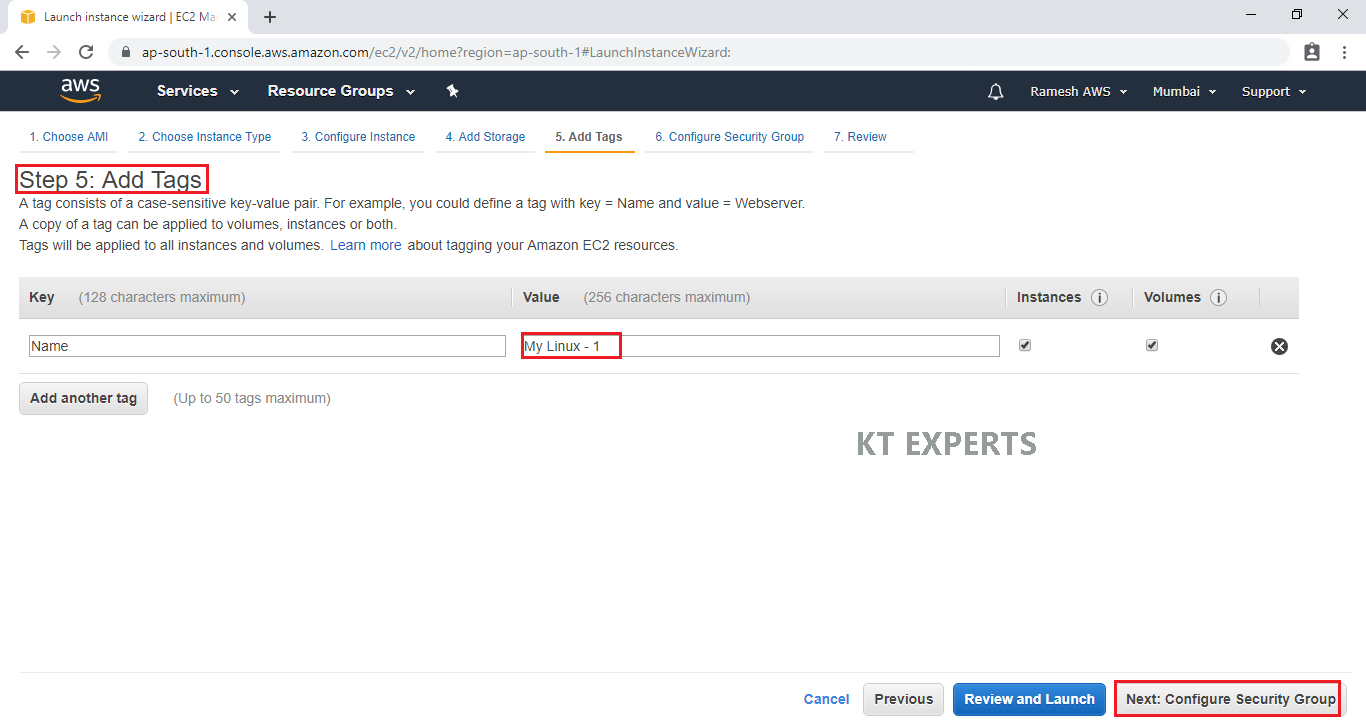
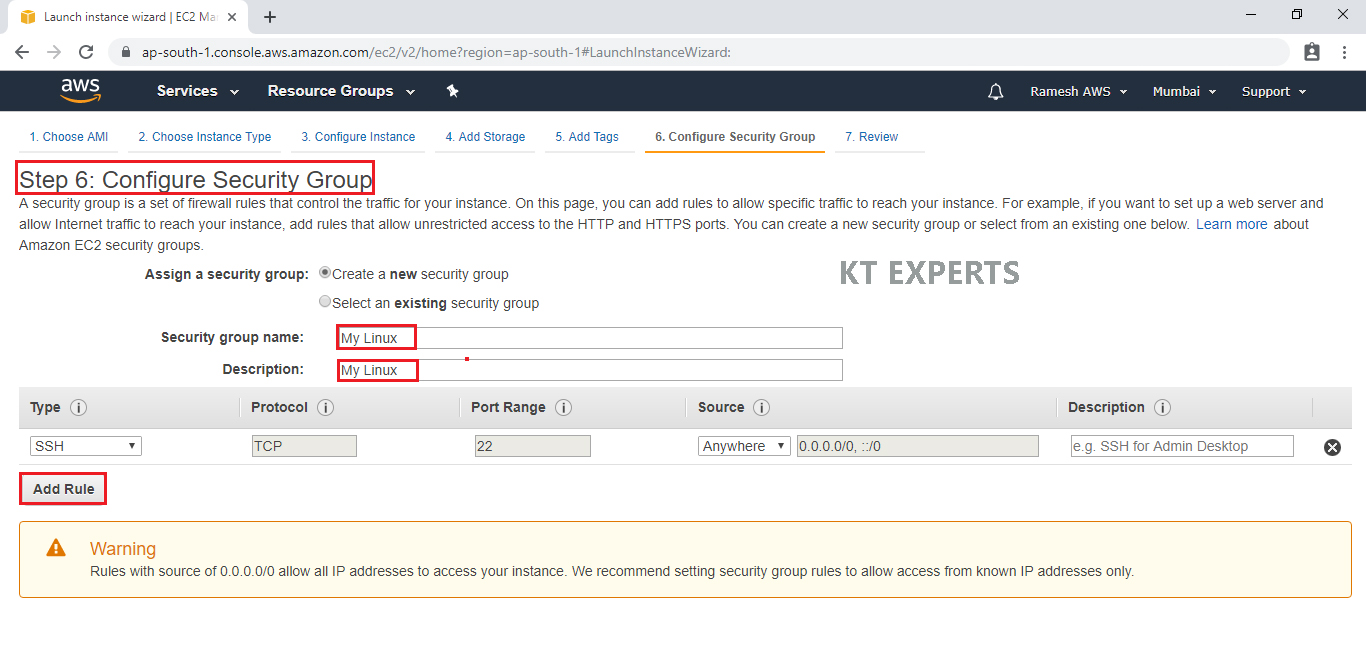
Configure Security Group
A security group allows configuring firewall rules to allow traffic as needed. Only one rule has been added to allow remote desktop connection.
SSH – Secure Shell
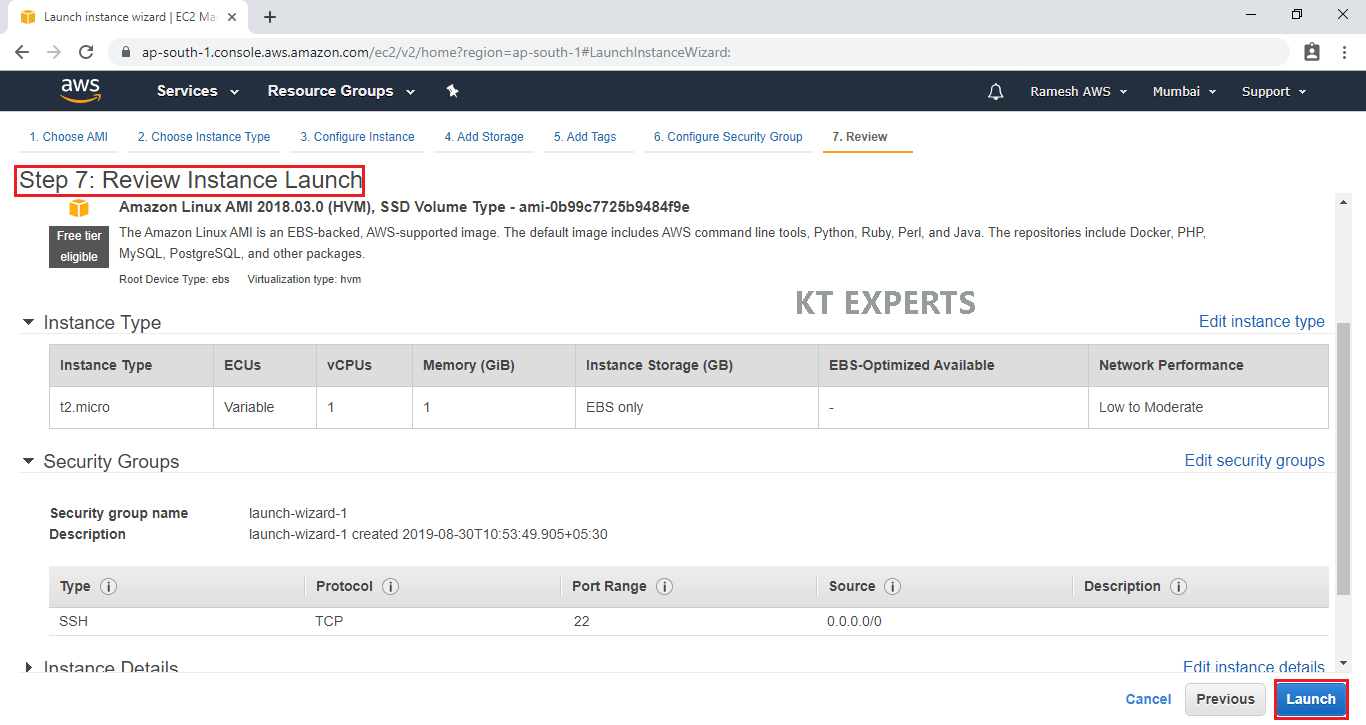
Review Instance Launch
Review and confirm the configuration of the instance. Click on the Edit button on each configuration item to make changes and click on Launch.
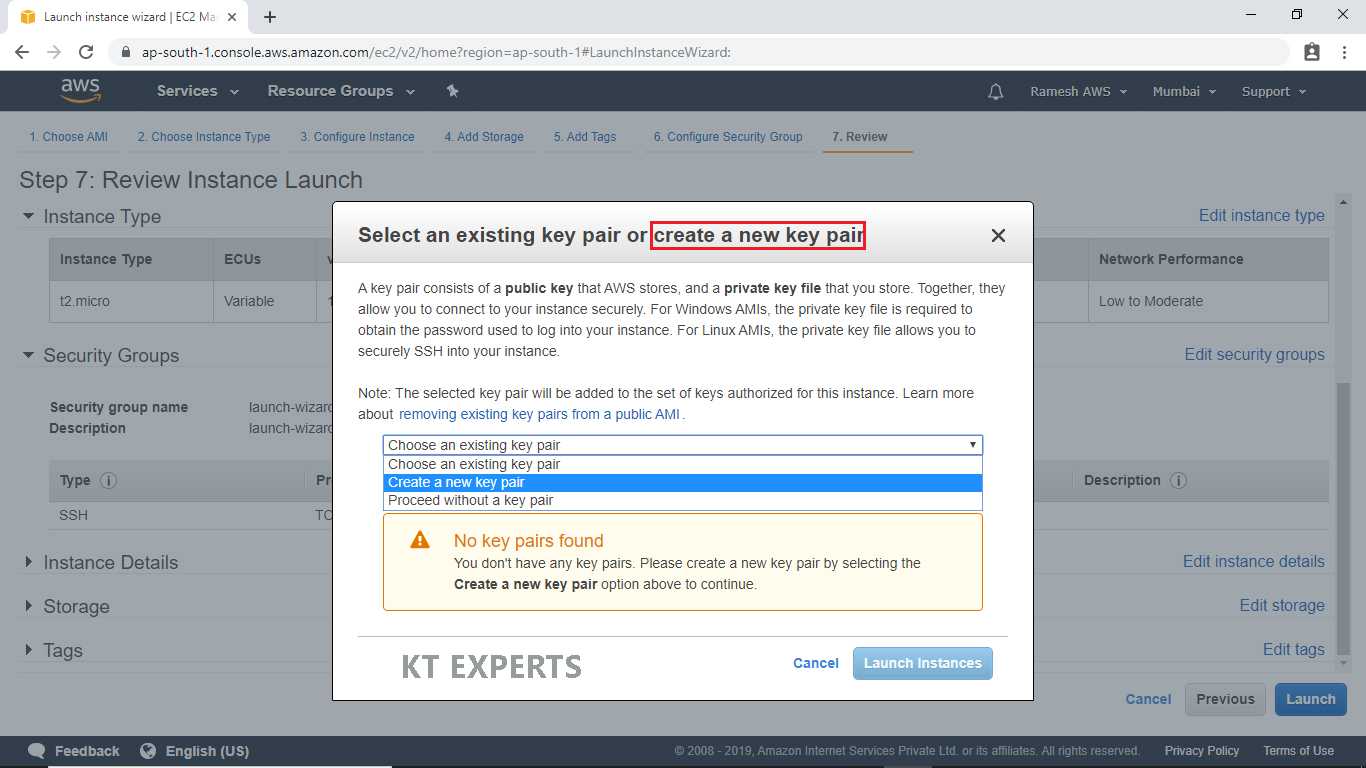
Create a Key Pair and Launch Your Instance
To connect to your virtual machine, you need a key pair. A key pair is used to log into your instance and select create a new key pair.
 Create a new key pair and name it My Linux. Then click Download Key Pair.
Create a new key pair and name it My Linux. Then click Download Key Pair.
After you have downloaded and saved your key pair, click Launch Instance to start your Windows Server instance.
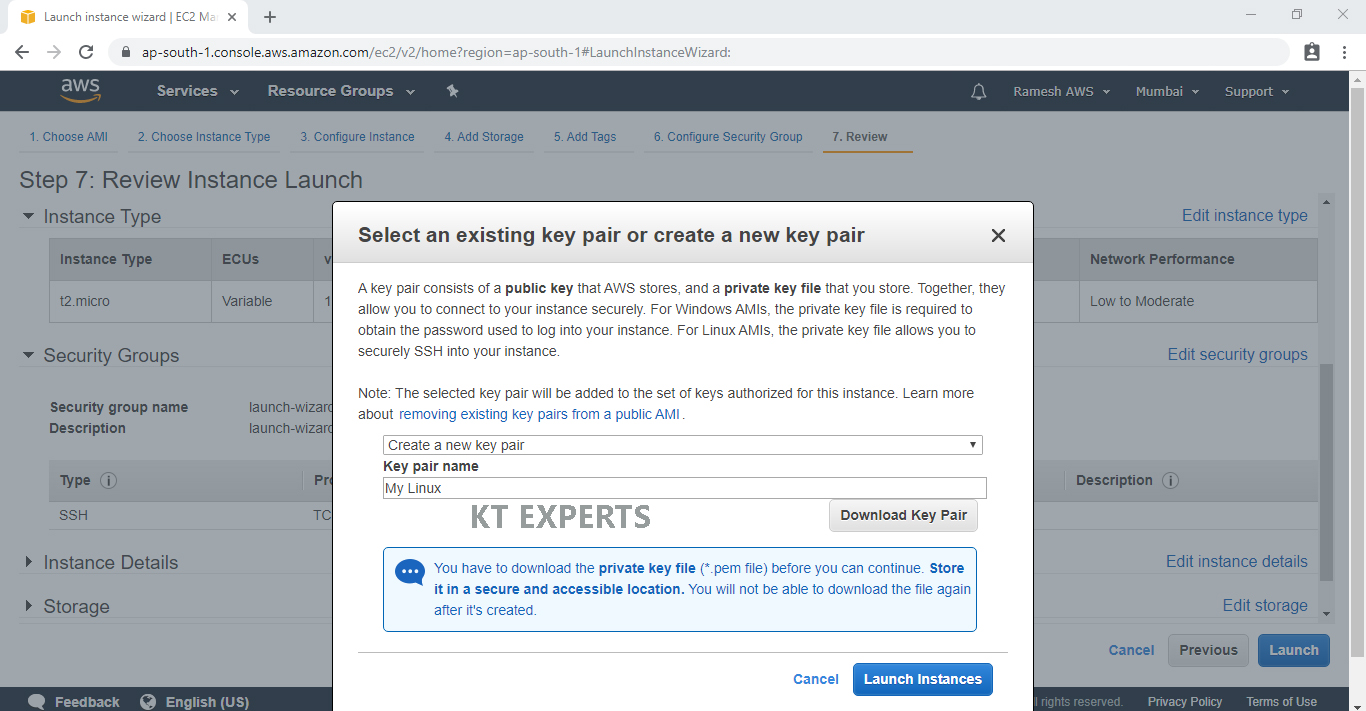
My Linux.pem will be downloaded to your computer — make sure to save this key pair in a safe location on your computer.
click on view Instances to view the instance you have just created and see its status.
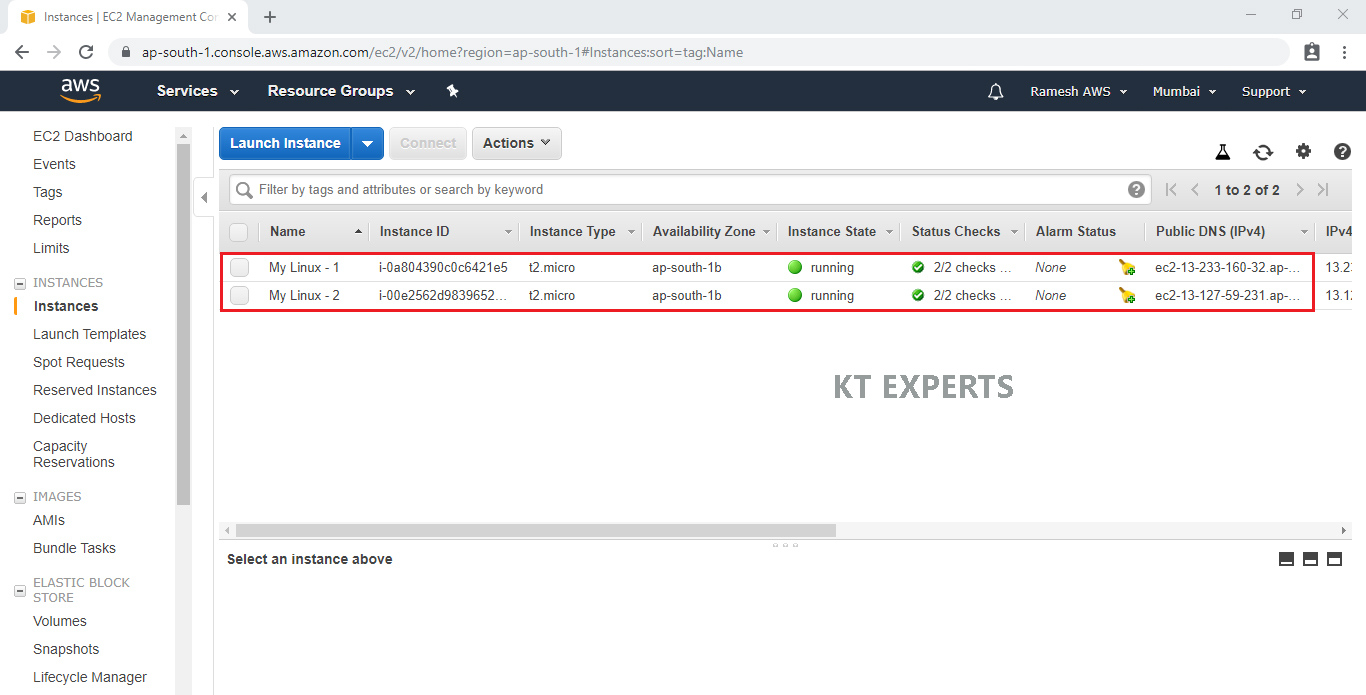
We can see 2 Linux virtual servers(EC2) which was created earlier.
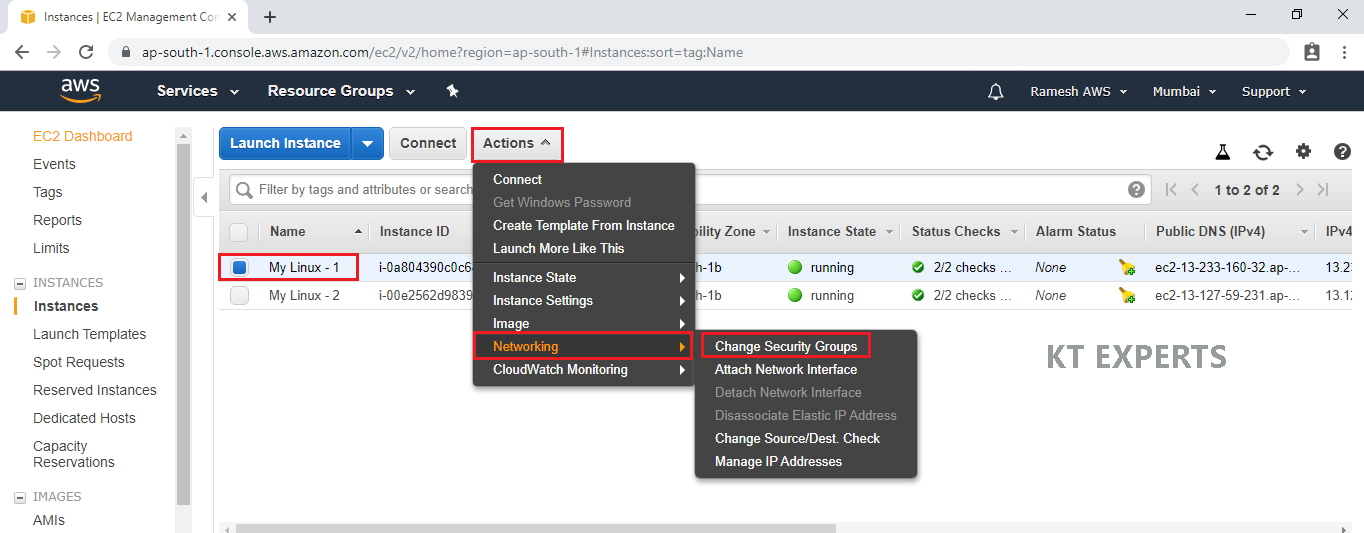
Assign default security group to Linux Server “Linux – 1”
Select first Linux virtual server “My Linux – 1”
In the Actions choose networking and click on change security groups.
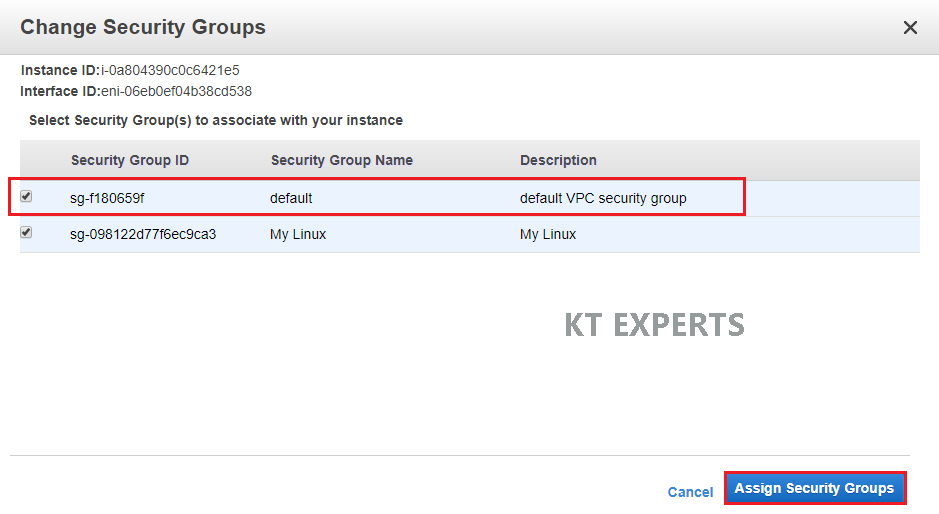
Select default security Group ID and click on Assign Security Groups.
Connect to First Linux Server “Linux – 1” terminal through putty

Provide default security group to Linux Server “Linux – 2”
Select first linux virtual server “My Linux – 2”
In the Actions choose networking and click on change security groups.
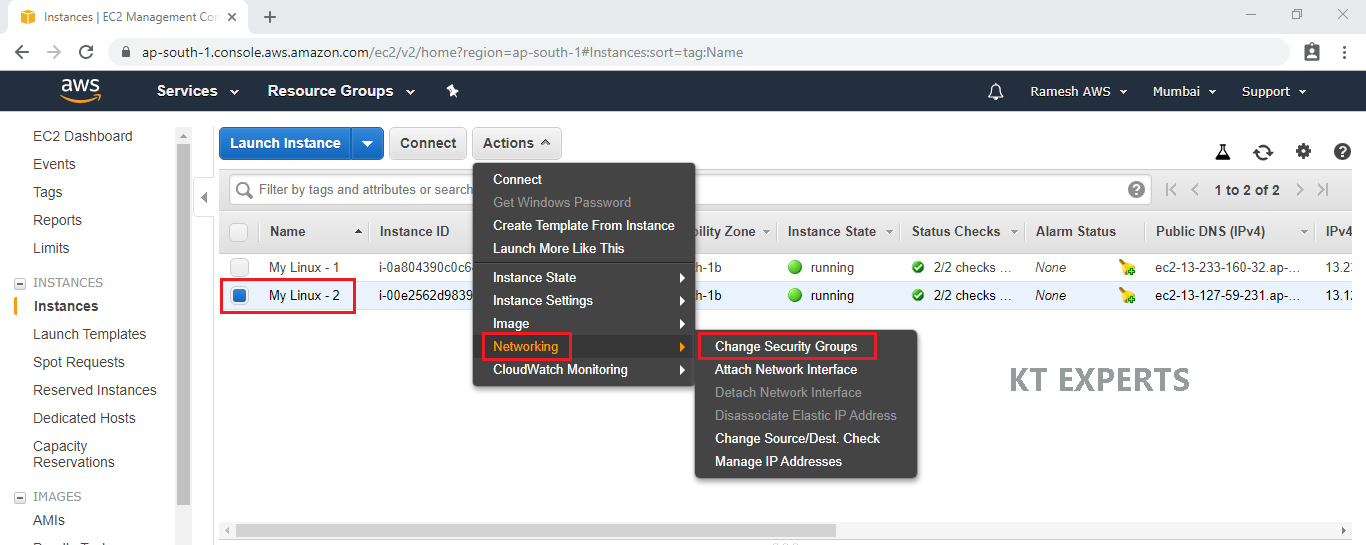
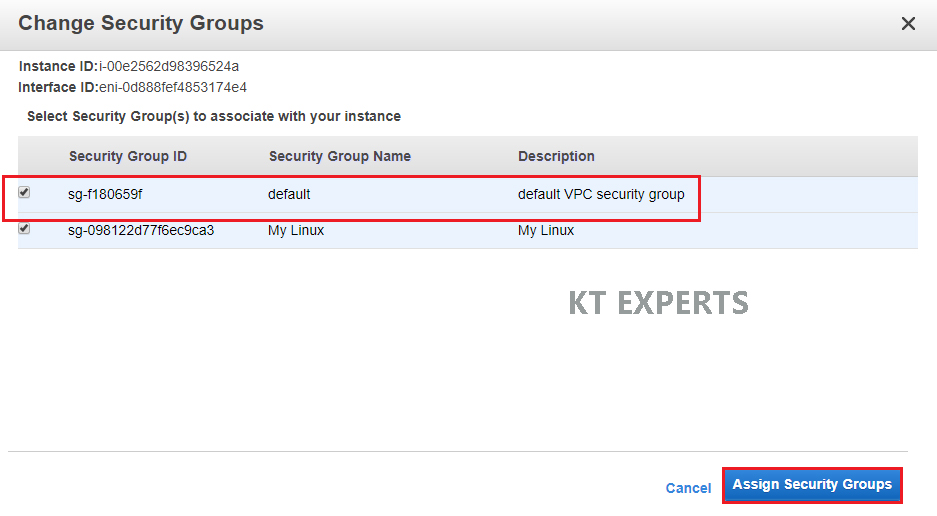
Select default security Group ID and click on Assign Security Groups.
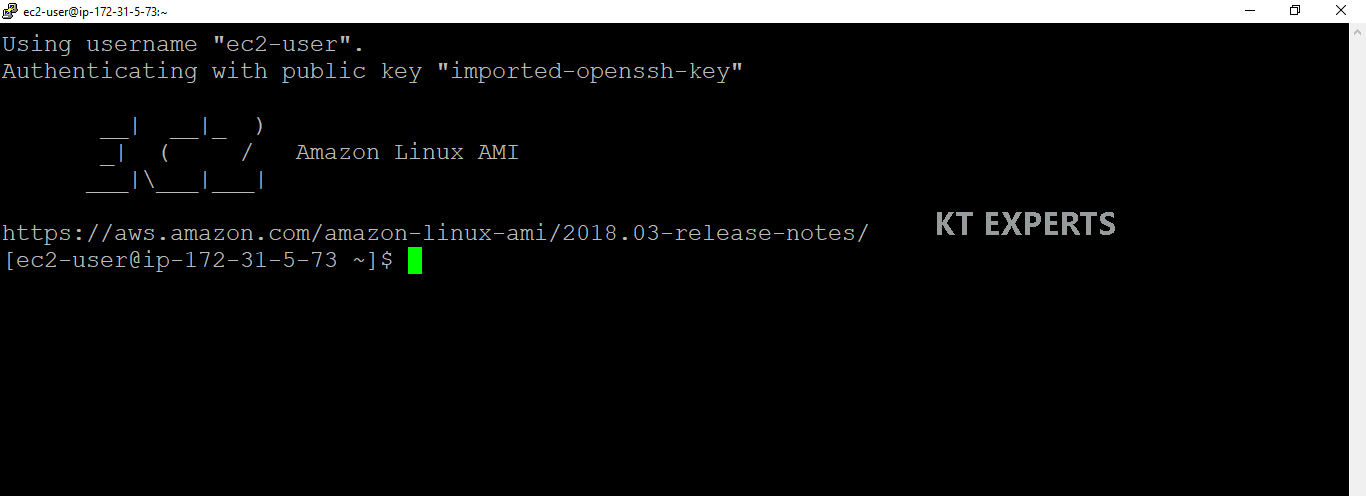
Connect to Second Linux Server “Linux – 2” terminal through putty
Create Mount point for first Linux Server “Linux – 1”
Go to First Linux Server terminal
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
Using username "ec2-user". Authenticating with public key "imported-openssh-key" __| __|_ ) _| ( / Amazon Linux AMI ___|\___|___| https://aws.amazon.com/amazon-linux-ami/2018.03-release-notes/ [ec2-user@ip-172-31-4-87 ~]$ |
Switch to root user
|
1 2 3 4 |
[ec2-user@ip-172-31-4-87 ~]$ sudo su [root@ip-172-31-4-87 ec2-user]# |
Make Mount Directory
Make Directory “ktexperts”
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
[root@ip-172-31-4-87 ec2-user]# mkdir ktexperts [root@ip-172-31-4-87 ec2-user]# ls Ktexperts |
Copy mount Command from EFS
Go to Services, Click on EFS in the Storage Module.
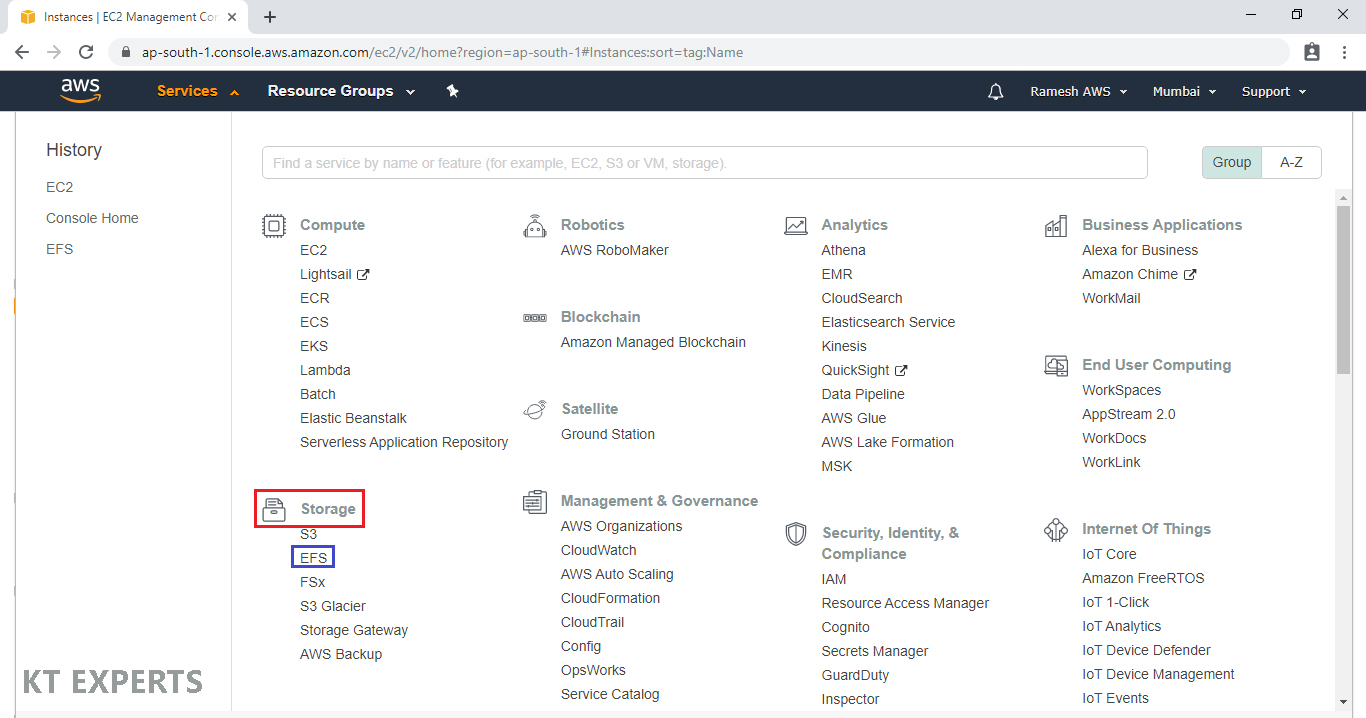
Click on Amazon EC2 mount instructions (from local VPC).
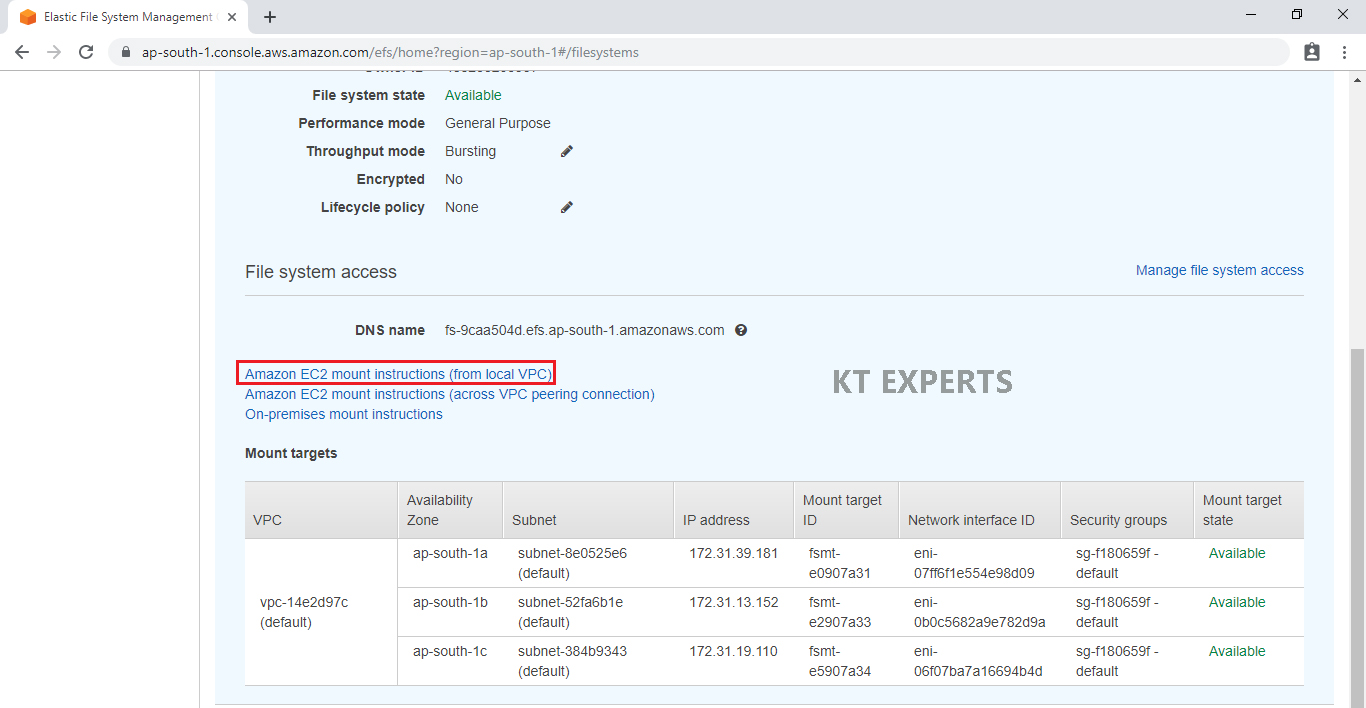
Copy command in the NFS Client.
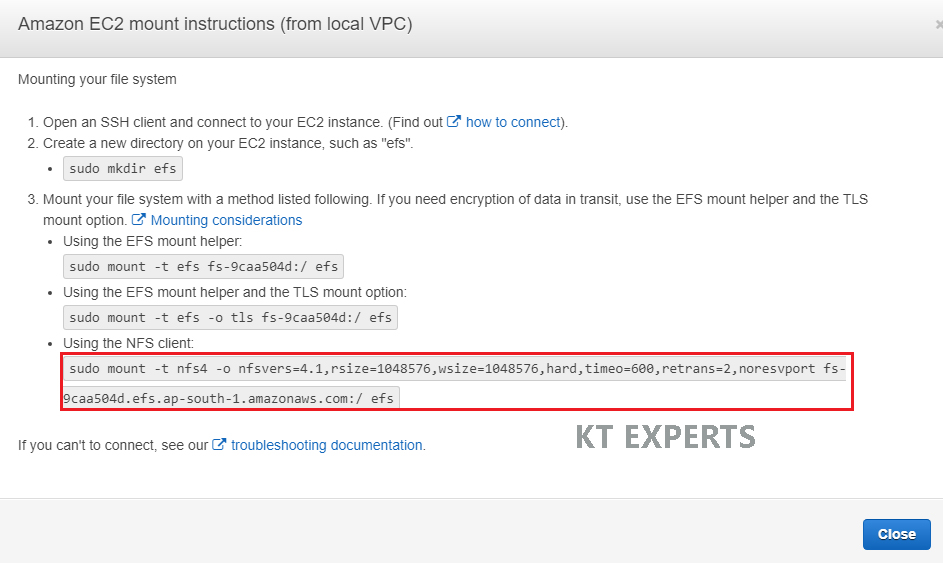
Paste Mount command in Linux terminal
Here,Replace efs with ktexpets for creating new mount point.
Note
To run command in root user we shouldn’t type sudo and in the normal user you should mention sudo before the command.
|
1 2 3 |
[root@ip-172-31-4-87 ec2-user]# mount -t nfs4 -o nfsvers=4.1,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576, hard,timeo=600,retrans=2,noresvport fs-9caa504d.efs.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com:/ ktexperts |
Make file in Mount Directory
Go to Mount directory ktexperts and make file
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
[root@ip-172-31-4-87 ec2-user]# cd ktexperts [root@ip-172-31-4-87 ktexperts]# touch aws [root@ip-172-31-4-87 ktexperts]# ls aws [root@ip-172-31-4-87 ktexperts]# |
Create Mount point for first Linux Server “Linux – 2”
Go to Second Linux Server terminal
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
Using username "ec2-user". Authenticating with public key "imported-openssh-key" Last login: Sat Sep 14 20:20:06 2019 from 124.123.103.5 __| __|_ ) _| ( / Amazon Linux AMI ___|\___|___| https://aws.amazon.com/amazon-linux-ami/2018.03-release-notes/ [ec2-user@ip-172-31-5-73 ~]$ |
Switch to root user
|
1 2 3 4 |
[ec2-user@ip-172-31-5-73 ~]$ sudo su [root@ip-172-31-5-73 ec2-user]# |
Make Mount Directory
Make Directory “micronet”
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
[root@ip-172-31-5-73 ec2-user]# mkdir micronet [root@ip-172-31-5-73 ec2-user]# ls micronet |
Copy mount Command from EFS
Copy command in the NFS Client.

Paste Mount command in Linux Server terminal
Here,Replace efs with ktexpets for creating new mount point.
Note
To run command in root user we shouldn’t type sudo and in the normal user you should mention sudo before the command.
|
1 2 3 |
[root@ip-172-31-5-73 ec2-user]# mount -t nfs4 -o nfsvers=4.1,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576, hard,timeo=600,retrans=2,noresvport fs-9caa504d.efs.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com:/ micronet |
Go to mount directory and check the files
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
[root@ip-172-31-5-73 ec2-user]# cd micronet [root@ip-172-31-5-73 micronet]# ls aws |
Note
Here, aws file came automatically because we created mount point for both servers.
whatever files create inside the mount directory it will be reflected to another server and vice versa.
Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the above information. Please click here to subscribe for further updates
KTEXPERTS is always active on below social media platforms.
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/ktexperts/
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/company/ktexperts/
Twitter : https://twitter.com/ktexpertsadmin
YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/c/ktexperts
Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/knowledgesharingplatform