Introduction to Chef (Configuration Management Tool)
In this article,we will see Introduction to Chef.

Configuration Management
It is a method through which we automate admin tasks.
Configuration management tool turns your code into infrastructure.
So your code would be testable, repeatable and versionable.
Infrastructure refers to the composite of —
Software
Network
People
Process
Pain Points
Management user and group accounts.
Dealing with packages.
Taking backup.
Deploying all kinds of applications.
Configure services.
Why configuration management tool?
Complete Automation.
Increase up time.
Improve performance.
Ensure compliance (Machines follow strict procedures).
Prevent errors (Machine won’t do any mistakes).
Reduces cost.
What is Chef?
Chef is a configuration management tool written in Ruby and Erlang.
It uses a pure-Ruby, domain-specific language (DSL) for writing system configuration recipes.
It is an open source configuration management tool developed by opscode.
It is written in Ruby and Erlang.

Chef is an automation tool that provides a way to define infrastructure as code.
Infrastructure as code (IAC) simply means that managing infrastructure by writing code (Automating infrastructure) rather than using manual processes.
It can also be termed as programmable infrastructure.
Chef uses a pure-Ruby, domain-specific language (DSL) for writing system configurations
It can be automated, tested and deployed very easily.
Chef has Client-server architecture.
It supports multiple platforms like Windows, Ubuntu, Centos, and Solaris etc.
Why Chef?
Chef is an administration tool.
Whatever system admins (windows/Linux) used to do manually.
Now , we are automating all those tasks by using chef (Any configuration management tool).
Example : water pots
Can use this tool whether your servers are in on-premises or in the cloud.
It turns your code into infrastructure.
Your computing environment has some of the same attributes as your application.
Your code is versionable, repeatable and testable.
You only need to tell what the desired configuration should be, not how to achieve it.
Through automation ,get desired state of server.
Large companies have a continually changing infrastructure that requires be configuring and maintaining time to time.
Chef provides:
Continuous deployment
Software is deployed continuously enabling a company to keep in pace with the market requirements.
Increases system robustness
Infrastructure automation ensures all bugs are caught and removed before deploying the software.
Adapt to the cloud
The chef is easily integrated with infrastructure on the cloud.
Entire infrastructure can be recorded in the form of a repository that can be used as a blueprint to recreate the infrastructure from scratch.
How Chef works?
Chef works on a three-tier client server model wherein the working units such as cookbooks are developed on the Chef workstation.
From the command line utilities such as knife, they are uploaded to the Chef server and all the nodes which are present in the architecture are registered with the Chef server.
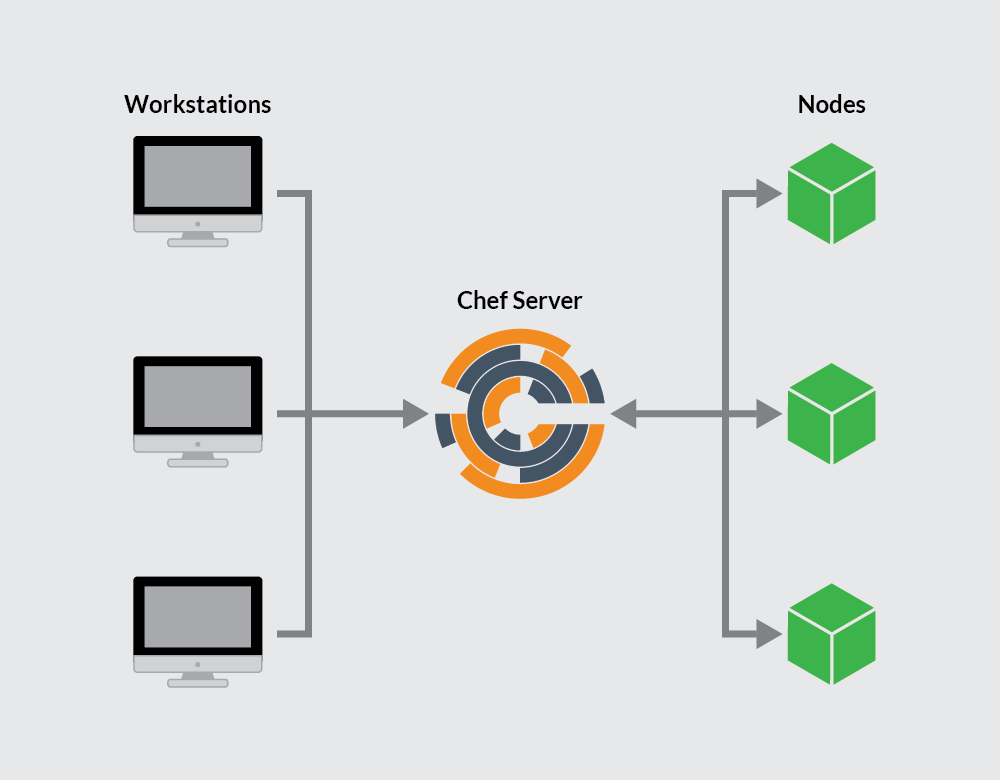
Chef basically consists of three components
Chef server
As the centre of operations, the Chef server stores, manages, and provides configuration data to all other Chef components.
Workstations
Workstations are personal computers or virtual servers where all configuration code is created, tested, and changed. There can be as many workstations as needed, whether this be one per person or otherwise.
Nodes
Nodes are the servers that are managed by Chef – these are the machines that changes are being pushed to, generally a fleet of multiple machines that require the benefits of automation.
Chef can manage nodes that are virtual servers, containers, network devices, and storage devices.
A Chef client is installed on every node that is under management by Chef.
These three components communicate in a mostly linear fashion, with any changes being pushed from workstations to the Chef server, and then pulled from the server to the nodes and implemented on each node via their Chef client.
In turn, information about the node passes to the server to determine which files are different from the current settings and need to be updated.
Chef Terminology
Chef Workstation — Where you write code.
Chef Server — Where you upload code.
Chef Node — Where you apply code.
Knife — It is a tool to establish a communication among workstation, servers and node.
Chef-Client — It is tool runs on every chef node to pull code from chef server.
Ohai — It is a system discovery tool.It will maintain current state information of chef node.
Idempotency — Tracking the state of system resources to ensure that the changes shouldn’t re-apply repeatedly.
Chef Supermarket — Where you get custom code.
Recipe — A file that contains a set of instructions (resources) to be executed. A recipe must be contained inside a Cookbook
Cookbook — A cookbook is a collection of recipes. They are the basic building blocks which get uploaded to Chef serve
Resource
It is the basic component of a recipe used to manage the infrastructure with different kind of states.
There can be multiple resources in a recipe, which will help in configuring and managing the infrastructure.
The following multiple resources are
package − Manages the packages on a node
service − Manages the services on a node
user − Manages the users on the node
group − Manages groups
template − Manages the files with embedded Ruby template
cookbook_file − Transfers the files from the files subdirectory in the cookbook to a location on the node
file − Manages the contents of a file on the node
directory − Manages the directories on the node
execute − Executes a command on the node
cron − Edits an existing cron file on the node
Metadata.rb — It is used to manage the metadata about the package. This includes details like the name and details of the package.
Benefits of Chef
Accelerating software delivery
when your infrastructure is automated all the software requirements like testing, creating new environments for software deployments etc. becomes faster.
Increased service Resiliency
By making the infrastructure automated it monitors for bugs and errors before they occur it can also recover from errors more quickly.
Risk Management
chef lowers risk and improves compliance at all stages of deployment. It reduces the conflicts during the development and production environment.
Cloud Adoption
Chef can be easily adapted to a cloud environment and the servers and infrastructure can be easily configured, installed and managed automatically by Chef.
Managing Data Centres and Cloud Environments
As discussed earlier Chef can run on different platforms, under chef you can manage all your cloud and on-premise platforms including servers.
Streamlined IT operation and Workflow
Chef provides a pipeline for continuous deployment starting from building to testing and all the way through delivery, monitoring, and troubleshooting.
Features of Chef
Easily manage hundreds of server with a handful of employees.
It can be easily managed using operating systems such as Linux, Windows, FreeBSD, and
It maintains a blueprint of the entire infrastructure.
It integrates with all major cloud service providers.
It is a centralized management.
A single Chef server can be used as the center for deploying the policies.
Chef functionalities
Infrastructure automation.
Cloud automation.
Automation for DevOps workflow.
Compliance and security management.
Automated workflow for Continuous Delivery.
Pros
One of the most flexible solutions for OS and middleware management.
Designed for programmers.
Strong documentation, support and contributions from an active community.
Very stable, reliable and mature, especially for large-scale deployments in both public and private environments.
Chef offers hybrid and SaaS solutions for Chef server, analytics and reporting.
Sequential execution order.
Cons
Requires a steep learning curve.
Initial setup is complicated.
Lacks push, so no immediate action on changes. The pull process follows a specified schedule.
Documentation is spread out, and it can become difficult to review and follow.
Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the above information. Please click here to subscribe for further updates
KTEXPERTS is always active on below social media platforms.
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/ktexperts/
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/company/ktexperts/
Twitter : https://twitter.com/ktexpertsadmin
YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/c/ktexperts
Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/knowledgesharingplatform





priya
Thanks for the good job. This really helps me.we want more articles on DevOps.
santhi
Interesting article on chef … nice job