Dear Readers,
In this article,we will see Brief Introduction on Git.

Source Code Management
SCM stands for Source Code Management is an integral part of any development project in the current IT world.
- Storage (Any code)
- Developers (Code)
- Testing Team (Test)
- DevOps (Scripts)
- Different people from different team can store simultaneously (Save all changes separately).
- Pipeline between offshore & on shore teams.
- Help in achieving teamwork.
- Track changes (Minute level).
- Source code is the storage where you store code.
- Whoever write the code they can store the code in SCM.
- Not only store the code but also we can manage the code.
- Source Management is a process we can achieve SCM by using SCM tools.
Source Code Management tools are the crucial ones that make or break the effort put in by multiple developer.
Types of Source Code Management (SCM) Tools
SCM Tools
- Git
- SVN
- Perforce
- ClearCase
Centralized Version Control System – SVN,Perforce,ClearCase
Distribution Version Control System – Git
Version Control System
A version control system (VCS) allows you to track the history of a collection of files.
It supports creating different versions of this collection.
Each version captures a snapshot of the files at a certain point in time.
VCS allows you to switch between these versions.
Version control systems are divided into two groups
Centralized Version Control Systems (CVCSs)
Distributed Version Control Systems (DVCSs)
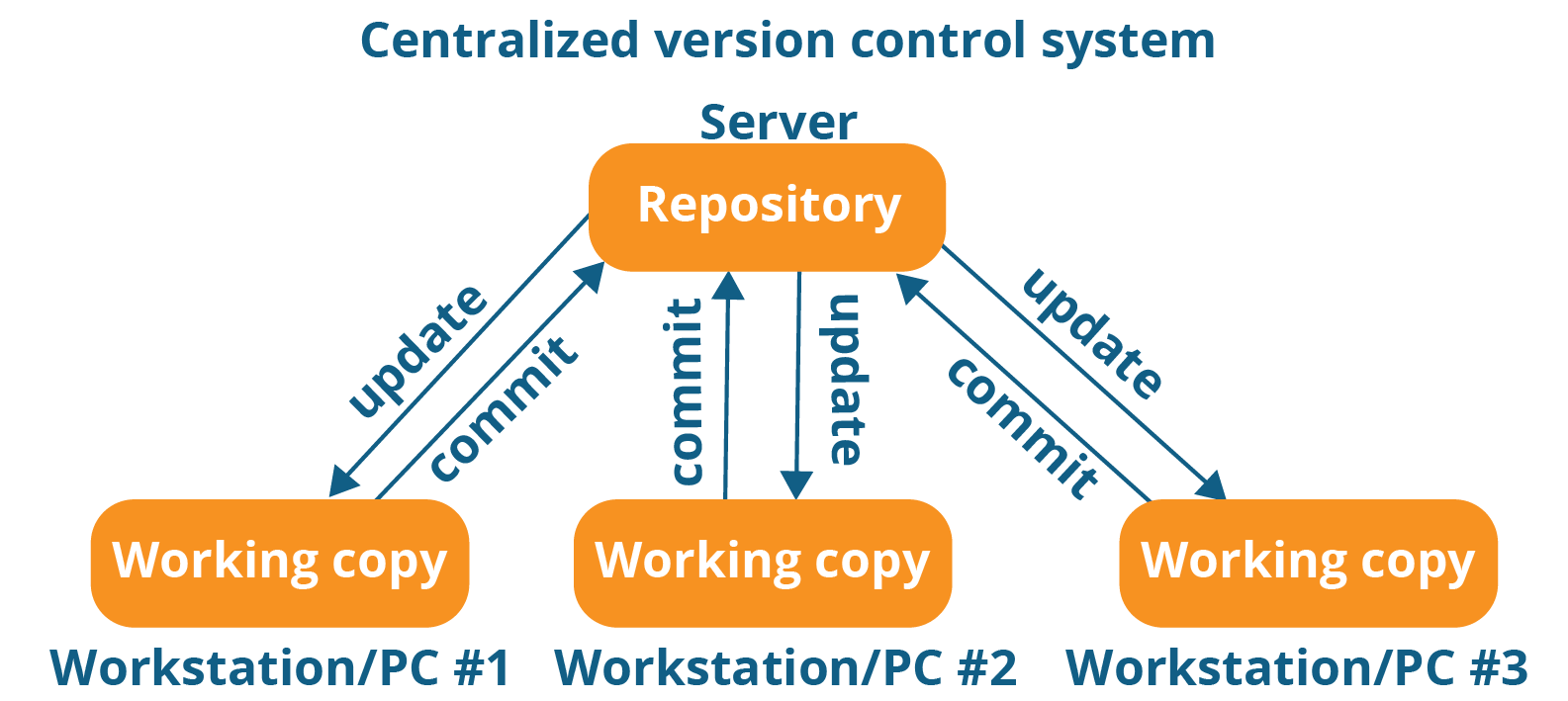
Centralized Version Control System
The concept of a centralized system is that it works on a Client-Server relationship.
The repository is located at one place and provides access to many clients.
Centralized Version Control Systems were developed to record changes in a central system and enable developers to collaborate on other systems.
 Advantages
Advantages
Relatively easy to set up
Provides transparency
Enable admins control the workflow
Disadvantages
If the main server goes down, developers can’t save versioned changes
Remote commits are slow
Unsolicited changes might ruin development
If the central database is corrupted, the entire history could be lost (security issues)
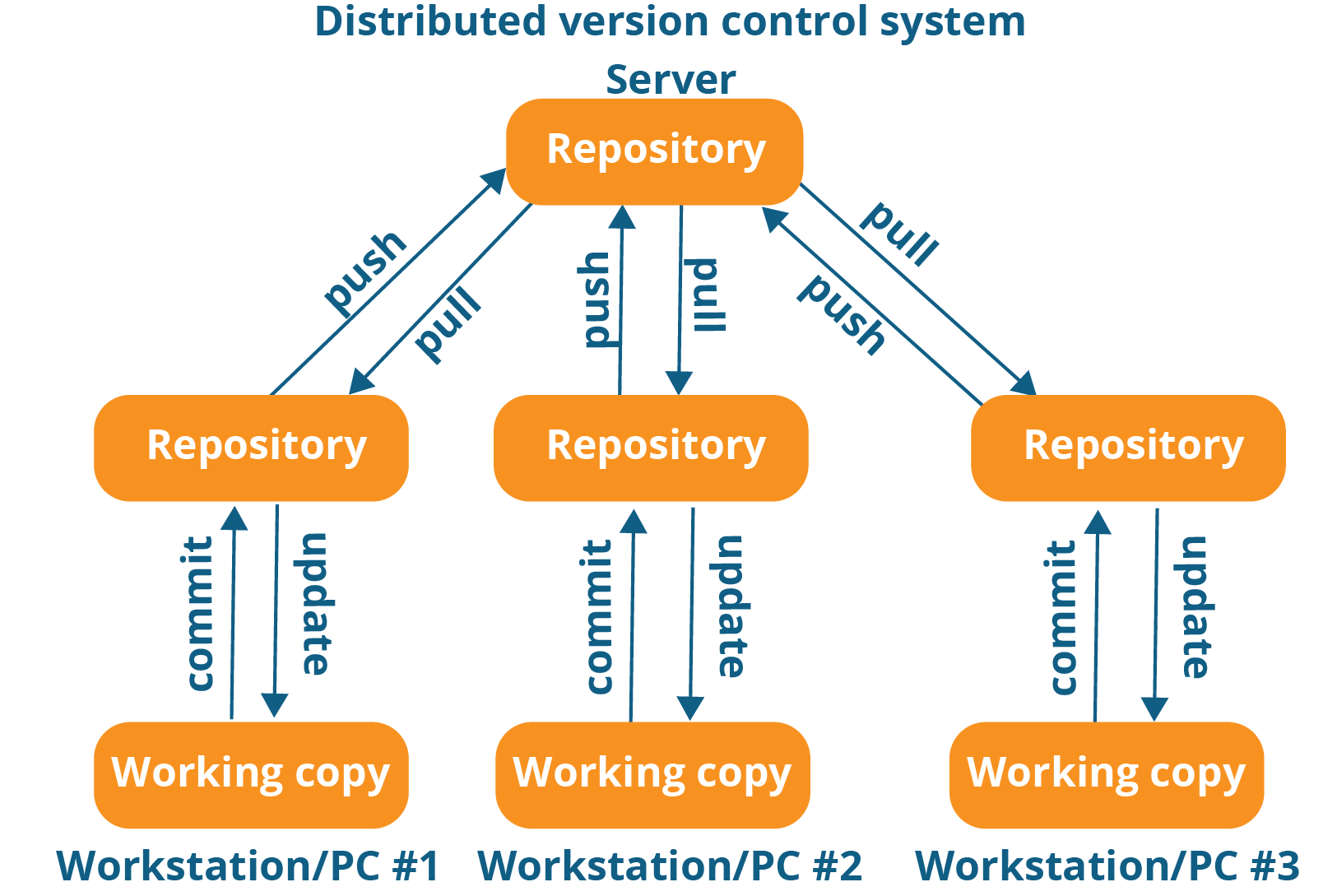
Distributed Version Control System
Git is an example of a distributed version control system (DVCS).
Commonly used for open source and commercial software development.
DVCSs allow full access to every file, branch, and iteration of a project.
Distributed Version Control Systems (DVCS) don’t rely on a central server.
Allows every user access to a full and self-contained history of all changes.
Each user has a complete local copy of a repository on his individual computer.
The user can copy an existing repository.
This copying process is typically called cloning and the resulting repository can be referred to as a clone.
Every clone contains the full history of the collection of files
Cloned repository has the same functionality as the original repository.
Advantages
Because of local commits, the full history is always available
No need to access a remote server (faster access)
Ability to push your changes continuously
Saves time, especially with SSH keys
Good for projects with offshore developers
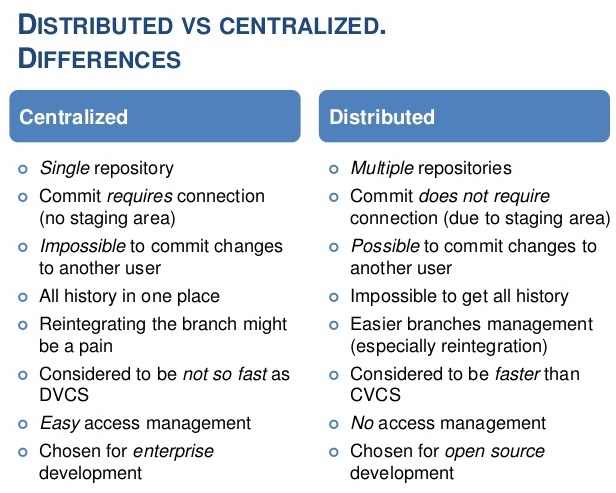
Differences Between Centralized Version Control Systems And Distributed Version Control Systems.
What is Git?
Git is currently the most popular implementation of a distributed version control system.
Git is commonly used for both open source and commercial software development, with significant benefits for individuals, teams and businesses.
Git originates from the Linux kernel development and was founded in 2005 by Linus Torvalds.
Nowadays it is used by many popular open source projects, e.g., the Android or the Eclipse developer teams, as well as many commercial organizations.
The core of Git was originally written in the programming language C.
Git has also been re-implemented in other languages, e.g., Java, Ruby and Python.
Git is a free software distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2.
According to the latest Stack Overflow developer survey, more than 70 percent of developers use Git.
Git Repository
A Git repository contains the history of a collection of files starting from a certain directory.
The process of copying an existing Git repository via the Git tooling is called cloning. After cloning a repository the user has the complete repository with its history on his local machine.
Types of Repositories
Bare Repositories (Central)
Store & share only.
All central repositories are bare repositories.
Non-Bare Repositories (Local)
Where you can modify the files.
All local repositories are Non-Bare Repositories.
Why Git?
Speed
Snapshot Concept.
Parallel branching
Multiple branches at a time unlike SCM tools.
Fully Distributed
Backup is available in multiple locations.
No need internet connection.so no network latency.
No need central server separately.
Each work space will have its own repo internally.
Can create any no of branches.
We can share code without using central repository.
That’s why we call GIT as DVCS (Distributed Version Control System).
Snapshots
Get any previous version (Backup).
Represents some data of particular time.
Stores the changes (appended data) only. Not whole copy.
Commit
Store changes in repository (Will get commit ID).
Commit ID contains 41 alpha numeric characters.
Concept-Checksum (It’s a tool in Linux generates binary value equal to data present in file).
Even if you change one dot, commit ID will changed.
Track changes.
Git Terminology
Repository
In Git we called as Repository.
It is a storage where we store our code.
It could be local repository or central repository.
In Git each copy of the repository is a complete repository.
Server – It is local Machine (EC2).
Work space
It is a place where you work like create files, write code etc.
Where you can see files physically and do modifications.
Branch
Product is same, so one repository but different tasks.
Each task has one separate task.
Finally merge (code) all branches.
For parallel development.
We can create any number of branches.
Changes are personal to that particular branch.
We can put files only in branches ( not in repository directly).
The default branch is “Master”.
Files created in workspace will be visible in any of the branch workspace until you commit.
Once you commit, then that file belongs to that particular branch.
Index
Index is an alternative term for the staging area.
Working tree
The working tree contains the set of working files for the repository. You can modify the content and commit the changes as new commits to the repository.
Commit
Sending the files from staging area to local repository that process we called commit.
Version/Version-ID/Commit-ID
Whenever you commit, you will get one commit ID.
It is reference to identify each change and who did that change.
It contains complete information regards to who has committed.
Tag
It is a meaning full name.
Whenever you commit, you will get one commit ID.
This commit ID contains 41 alphanumeric characters, so we can’t remember commit ID.
For easier understanding we give tag for the commit ID.
Git Stages
Work Space
It is a place where you work like create files, write code etc.
Where you can see files physically and do modifications.
Staging Area
The file has been added to git’s version control but changes have not been committed.
Buffer area
The file has been added to git’s version control, it will take snapshot (Incremental) immediately.
Repository (Local)
Store changes Locally.
Repository (Central)
Store changes Centrally
Key Points
untracked
The file is not tracked by the Git repository. This means that the file never staged nor committed.
Tracked
committed and not staged
staged
The file has been added to git’s version control but changes have not been committed.
Committed
The change has been committed.
Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the above information. Please click here to subscribe for further updates
KTEXPERTS is always active on below social media platforms.
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/ktexperts/
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/company/ktexperts/
Twitter : https://twitter.com/ktexpertsadmin
YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/c/ktexperts
Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/knowledgesharingplatform
Follow Me
Ramesh’s Linkedin : https://www.linkedin.com/in/ramesh-atchala/





Priya
Useful and knowledge gained
santhi
Good article and nice presentation with full of information and expecting more articles