Dear Readers,
In this articles we will see RAC : Oracle Grid Infrastructure.

The Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a standalone server is the Oracle software that provides system support for an Oracle database including volume management, file system, and automatic restart capabilities.
If you plan to use Oracle Restart or Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM), you must install Oracle Grid Infrastructure before installing your database.
Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a standalone server is the software that includes Oracle Restart and Oracle ASM.
Oracle combined the two infrastructure products into a single set of binaries that is installed as the Oracle Grid Infrastructure home. Oracle Grid Infrastructure should be installed before installing Oracle Database 11g Release 2.
Oracle RAC was started in 9i version
In 9i version of oracle its started as cluster manager
9i ——-> Cluster manager
In 10gR1 version of oracle RAC changed to CRS S/W
10gR1 ——-> CRS S/W
In 10gR2 version of oracle its named as Clusterware
10gR2 ——-> Clusterware
11gR1 ——-> Clusterware
In 11gR2 version of oracle clusterware changes to Grid Infrastructure Services
11gR2 ——-> Grid Infrastructure Services
In 11gR2, ASM and Oracle Clusterware are installed into a single home directory called the Grid Infrastructure home.
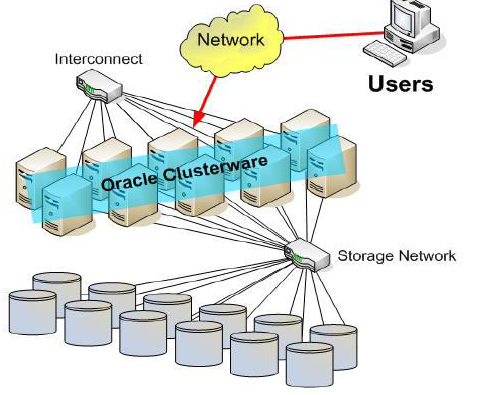
Oracle Clusterware
- Oracle Clusterware is: –
- A key part of Oracle Grid Infrastructure
- Integrated with Oracle Automatic Storage Management (ASM) – from 11gR2
- The basis for ASM Cluster File System (ACFS) – from 11gR2
- A foundation for Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC)
- A generalized cluster infrastructure for all kinds of applications
Please check below image to clear Idea on Clusterware
RAC Software Principles: –
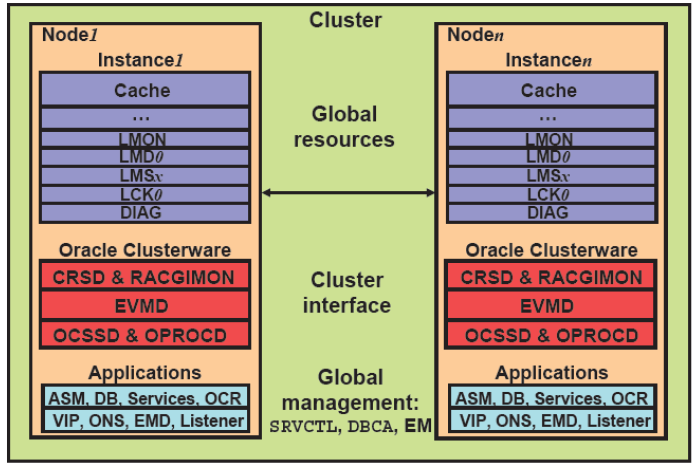
Here we are talking about 2 Node RAC Environment.
Here, few additional background processes associated with a RAC instance.
These processes are primarily used to maintain database coherency among each instance.
They are called as global resources: –
- LMON: Global Enqueue Service Monitor
- LMD0: Global Enqueue Service Daemon
- LMSx: Global Cache Service Processes, where x can range from 0 to j
- LCK0: Lock process
- DIAG: Diagnosability process
Main processes of Oracle Clusterware: –
- CRSD and RACGIMON: Are engines for high-availability operations
- OCSSD: Provides access to node membership and group services
- EVMD: Scans callout directory and invokes callouts in reactions to detected events
- OPROCD: Is a process monitor for the cluster
Other Components / Resources: –
- Automatic Storage Management (ASM) instances
- RAC databases
- Services and node applications.
RAC Software Storage Principles: –
Here we will talk about storage related information
The Oracle Database 11g Real Application Clusters installation is a two-phase installation.
In the first phase, you install Oracle Clusterware. In the second phase, you install the Oracle database software with RAC components and create a cluster database.
Oracle Clusterware includes two important components: the voting disk and the OCR.
Voting Disk :
The voting disk is a file that manages information about node membership, each voting disk must be accessible by all nodes in the cluster.
If any node is not passing heat-beat across other node or voting disk, then that node will be evicted by Voting disk.
Oracle Cluster Registry :
The OCR is a file that manages cluster and Oracle RAC database configuration information such as RAC database, listener, VIP, Scan IP & Services.
Note :
The Oracle Clusterware installation process creates the voting disk and the OCR on shared storage.
Important lines of OCR & VOTING DISK :
If you select the option for normal redundant copies during the installation process, then Oracle Clusterware automatically maintains redundant copies of these files to prevent the files from becoming single points of failure.
When you use normal redundancy, Oracle Clusterware automatically maintains two copies of the OCR file and three copies of the voting disk file.
We can store the software storage in two methods.
First Method :
Keeping CRS_HOME,ASM_HOME and ORACLE_HOME in each and every node in a cluster.
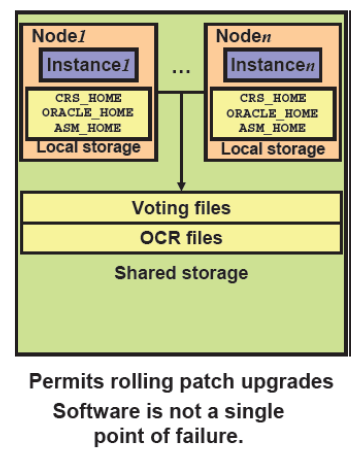
In above image CRS and ASM and ORACLE home locations kept under in both the Nodes. In this case when ever a particular node goes down user can connect from another node . Because all software are available at all the nodes in a cluster.
Here we can achieve high availability on instance level.
Second Method :
Keeping ORACLE_HOME and ASM_HOME in Shared Storage and CRS_HOME will be available on all instances in a cluster.
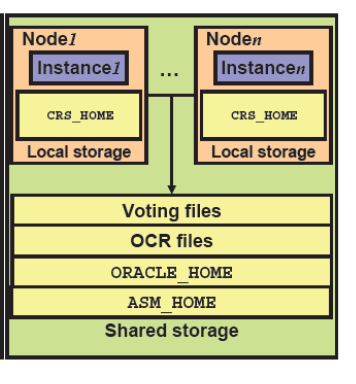
In Case of any patching or update activity we have downtime because of ORACLE_HOME and ASM_HOME are in shared storage.
In patching activity or update activity Oracle should be shutdown in that case users cant access database RAC database from Shared Storage.
RAC Software Storage Principles (Physical files) : –
The primary difference between RAC storage and storage for single-instance Oracle databases is that all data files in RAC must reside on shared devices (either raw devices or cluster file systems) in order to be shared by all the instances that access the same database.
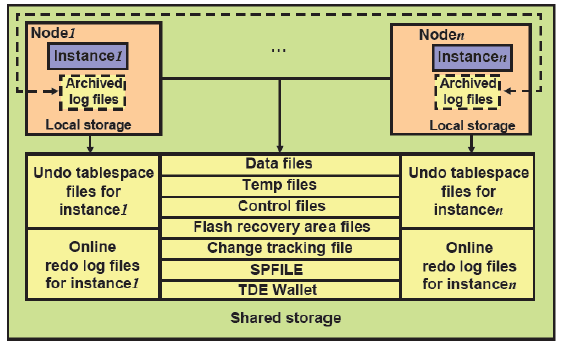
You must also create atleast two redo log groups for each instance, and all the redo log groups must also be stored on shared devices for instance or crash recovery purposes.
Each instance’s online redo log groups are called an instance’s thread of online redo.
In addition, you must create one shared undo tablespace for each instance for using the recommended automatic undo management feature.
Each instance’s undo tablespace must be shared by all other instances for recovery purposes.
Archive logs cannot be placed on raw devices because their names are automatically generated and are different for each archive log. That is why they must be stored on a file system.
If you use cluster file system (CFS), it enables you to access these archive files from any node at any time.
If you do not use a CFS, you are always forced to make the archives available to the other cluster members at the time of recovery—for example, by using a network file system (NFS) across nodes.
If you are using the recommended flash recovery area feature, then it must be stored in a shared directory so that all instances can access it.
Note:
A shared directory can be an ASM disk group, or a cluster file system
Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the above information. Please click here to subscribe for further updates
KTEXPERTS is always active on below social media platforms.
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/ktexperts/
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/company/ktexperts/
Twitter : https://twitter.com/ktexpertsadmin
YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/c/ktexperts



Sheetal Kothari
Nice article….it’s helpful for beginners also. Thanks Ajay for this article.